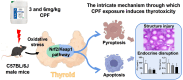
Subchronic Chlorpyrifos Exposure Induces Thyroid Follicular Cell Pyroptosis to Exacerbate Thyroid Toxicity by Modulating Nrf2/Keap1/NF-κB Pathway in Male Mice
- PMID: 40692545
- PMCID: PMC12277183
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S523861
Subchronic Chlorpyrifos Exposure Induces Thyroid Follicular Cell Pyroptosis to Exacerbate Thyroid Toxicity by Modulating Nrf2/Keap1/NF-κB Pathway in Male Mice
Abstract
Purpose: Chlorpyrifos (CPF), a widely used organophosphate pesticide in agriculture, particularly in China, has raised significant environmental and health concerns due to its persistence and bioaccumulation. While CPF-induced toxicity in multiple organ systems has been documented, its long-term impact on thyroid homeostasis and the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the subchronic effects of CPF on thyroid function and elucidate the underlying mechanisms of CPF-induced thyroid toxicity.
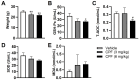
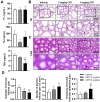
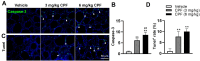
Methods: The study utilized 4-week-old male C57BL/6J mice as experimental subjects. These mice were exposed to CPF via intragastric gavage at doses of 3 or 6 mg/kg for a duration of 8 weeks. Throughout the study period, various parameters were assessed, including body weight, serum antioxidant capacity, thyroid endocrine function and structure, apoptosis markers, inflammatory cytokines, and relevant molecular pathways.
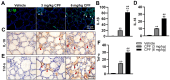
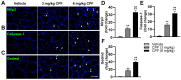
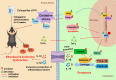
Results: The study revealed that CPF exposure resulted in significant systemic toxicity, manifested through reduced body weight and impaired serum antioxidant capacity. Examination of thyroid-specific effects showed disrupted thyroid endocrine function and structure, accompanied by increased apoptosis and elevated inflammatory cytokines. At the molecular level, CPF significantly stimulated thyroid follicle cell pyroptosis by upregulating the expression of Nlrp3, Caspase-1, and Gsdmd. Further mechanistic analysis demonstrated that CPF activated thyroid follicular cell pyroptosis by modulating the Nrf2/Keap1 antioxidative pathway and enhancing phosphorylation of p65 via NF-κB signaling.
Conclusion: This comprehensive investigation provides novel insights into the mechanisms of CPF-induced thyroid toxicity. The findings demonstrate that CPF exposure compromises thyroid homeostasis through the induction of follicular cell pyroptosis and modulation of the Nrf2/Keap1/NF-κB signaling axis, highlighting the potential health risks associated with CPF exposure and its impact on thyroid function.
Keywords: Nrf2/Keap1/NF-κB pathway; chlorpyrifos; pyroptosis; thyroid follicular cell; thyroid toxicity.
© 2025 Gu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- John EM, Shaike JM. Chlorpyrifos: pollution and remediation. Environ Chem Lett. 2015;13(3):269–291. doi: 10.1007/s10311-015-0513-7 - DOI
-
- Arain M, Brohi M, Channa A, et al. Analysis of chlorpyrifos pesticide residues in surface water, ground water and vegetables through gas chromatography. J Int Environ Appl Sci. 2018;13:167.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

