Randomised controlled trial: nutritional supplements to relieve irritable bowel syndrome symptoms by targeting the gut microbiota
- PMID: 40692549
- PMCID: PMC12278178
- DOI: 10.1017/jns.2025.10021
Randomised controlled trial: nutritional supplements to relieve irritable bowel syndrome symptoms by targeting the gut microbiota
Abstract
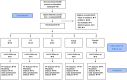
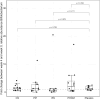
In individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), eliminating dietary triggers can alleviate symptoms but may lead to nutrient deficiencies and overall health decline. Although various nutritional supplements show promising results in relieving IBS symptoms due to their potential to alter the microbiome, conclusive scientific evidence remains lacking. This exploratory study aims to assess the bifidogenic properties of four nutritional supplement interventions and their impact on IBS-symptoms, faecal microbiota composition, faecal short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) concentrations, stool pattern, and quality of life (QoL), compared to a placebo control. Seventy subjects with IBS, meeting the ROME IV criteria, participated in this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel intervention study. Subjects were assigned to one of the four treatment groups, receiving either resistant starch, pea fibre, chondroitin sulfate, protein hydrolysate, or placebo daily for four weeks. Daily reports on stool pattern and gastrointestinal complaints were collected. Stool samples and questionnaires on dietary intake, symptom severity, QoL, and anxiety and depression were collected at baseline and after the 4-week intervention. The results show no significant increase in Bifidobacterium abundance or faecal SCFA levels after the 4-week intervention with any of the four nutritional supplement interventions. While some improvements in symptom severity and QoL were observed within-groups, these were not significantly different from changes observed with placebo. In conclusion, the tested nutritional supplements did not increase Bifidobacterium abundance in subjects with IBS within four weeks. Furthermore, we conclude that future studies should consider a run-in period and a larger sample size to study improvements in IBS symptoms.
Keywords: BMI, Body Mass Index; Bifidobacterium; EMA, Ecological Momentary Assessment; FDR, False Discovery Rate; FFQ, Food Frequency Questionnaire; Functional foods; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Score; IBS, Irritable bowel Syndrome; IBS-C, IBS with predominant constipation; IBS-D, IBS with predominant diarrhoea; IBS-M, IBS with a mix of constipation and diarrhoea; IBS-SSS, Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scoring System; IBS-U, IBS with no specific stool pattern; ITT, Intention To Treat; Irritable bowel syndrome; Microbiota; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; PP, Per protocol; QoL, quality of life; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids; severity.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare not to have conflict of interest. No brand names or specific products were communicated to the study subjects.
Figures


References
-
- Drossman DA. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1262–1279.e2. - PubMed
-
- Ohman L, Simren M. Pathogenesis of IBS: role of inflammation, immunity and neuroimmune interactions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(3):163–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

