Dietary supplementation with glutamate improves the flesh quality of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) by altering muscle texture characteristics and increasing the deposition of flavour substances
- PMID: 40692551
- PMCID: PMC12278179
- DOI: 10.1017/jns.2025.10009
Dietary supplementation with glutamate improves the flesh quality of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) by altering muscle texture characteristics and increasing the deposition of flavour substances
Abstract
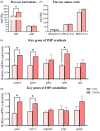
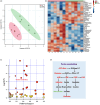
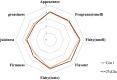
Nutrition intervention is an effective way to improve flesh qualities of fish. The effect of feed supplementation with glutamate (Glu) on flesh quality of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) was investigated. In trial 1, the fish (initial weight: 37.49 ± 0.08 g) were fed two practical diets with 0 and 2% Glu supplementation. In trial 2, the fish (37.26 ± 0.04 g) were fed two purified diets with 0 and 3% Glu supplementation. The results after feeding trials showed that dietary Glu supplementation increased the hardness and springiness of muscle, whether using practical or purified diets. Glu-supplemented diets increased the thickness and density of myofibres and collagen content between myofibres. Furthermore, Glu promoted muscle protein deposition by regulating the IGF-1-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway, and enhanced the myofibre hypertrophy by upregulating genes related to myofibre growth and development (mef2a, mef2d, myod, myf5, mlc, tpi and pax7α). The protein deposition and myofibre hypertrophy in turn improved the flesh texture. In addition, IMP content in flesh increased when supplementing Glu whether to practical or to purified diet. Metabolomics confirmed that Glu promoted the deposition of muscle-flavoured substances and purine metabolic pathway most functioned, echoed by the upregulation of key genes (ampd, ppat and adsl) in purine metabolism. The sensory test also clarified that dietary Glu improved the flesh quality by enhancing the muscle texture and flavour. Conclusively, dietary Glu supplementation can improve the flesh quality in this fish, which can further support evidence from other studies more generally that improve flesh quality of cultured fish.
Keywords: 4e-bp2, eukaryotic translation factor 4E-binding protein 2; AKT, protein kinase B; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; CWL, centrifugal weight loss; FAA, flavour amino acids; FBW, final body weight; FE, feed efficiency; FR, feeding rate; Flavour; Flesh quality; GMP, guanosine monophosphate; Glu, glutamate; Glutamate; HSI, hepatosomatic index; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IMP, inosine monophosphate; MRFs, myogenic regulatory factors; Myf, myogenic factor; MyoD, myoblast determination protein; Myofibre; Myog, myogenin; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; S6, ribosomal protein s6; SGR, specific growth rate; SR, survival rate; TOR, target of rapamycin; Texture; adsl, adenylosuccinate lyase; adss, adenylosuccinate synthetase; ampd, AMP deaminase 2; atic, bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein; cast, calpastatin; eif4e, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; gcn2, general control nonderepressible 2; gmps, GMP synthase.; impdh1, inosine5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1; mef, myocyte-specific enhancer factor; mlc, myosin light chain; mstn, myostatin; nt5c3, 5’-nucleotidase III; pax, paired box; pfas, phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase; pnp, purine nucleoside phosphorylase; ppat, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase; s6k1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; samd, SMAD family member; tpi, troponin I; tpt, troponin T.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Melatonin supplementation to sows in mid to late gestation affects offspring circadian, myogenic, and growth factor transcript abundance in pre and postnatal skeletal muscle.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae377. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae377. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39679952
-
Enhancing skeletal muscle fiber characteristics, intramuscular fat deposition, and fatty acid composition in broilers under heat stress through combined selenomethionine and Bacillus subtilis supplementation in the diet.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae267. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae267. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39301922
-
Diammonium phosphate supplementation in low-protein diets enhances growth performance in growing pigs without compromising carcass traits and meat quality.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf088. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf088. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40125885
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024 – Blue Transformation in Action. Rome: FAO; 2024.
-
- Liu XW, Feng L, Jiang WD, et al. (2-Carboxyethyl) dimethylsulfonium bromide (Br-DMPT) improves muscle flesh quality and antioxidant status of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed non-fish meal diets. Aquaculture. 2020;521:735065.
-
- Moreno HM, Montero MP, Gómez-Guillén MC, et al. Collagen characteristics of farmed Atlantic salmon with firm and soft fillet texture. Food Chem. 2012;134(2):678–685. - PubMed
-
- Song D, Yun Y, He Z, et al. Fillet texture, physicochemical indexes, muscle cellularity and molecular expression in muscle of Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus) in response to dietary hydroxyproline supplementation. Aquaculture. 2022;549:737783.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

