Nonlinear association between gamma-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and risk of progression from normoglycemia to prediabetes: a 5-year cohort study
- PMID: 40692596
- PMCID: PMC12277162
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1552044
Nonlinear association between gamma-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and risk of progression from normoglycemia to prediabetes: a 5-year cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Current research on the association between the Gamma-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein ratio (GHR) and the risk of prediabetes (pre-DM) remains scarce. This study aims to explore the potential link between GHR and the risk of progression from normoglycemia to pre-DM.
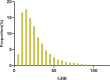
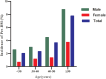
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 8,168 individuals who voluntarily underwent health examinations at Shenzhen Dapeng New District Kuichong People's Hospital between January 2018 and December 2023. To assess the association between GHR and the risk of developing pre-DM, Cox proportional hazards regression models were employed. Cox proportional hazards regression model with cubic spline function was further utilized to investigate potential nonlinear association. Moreover, a competing risk Cox proportional hazards model was applied to account for the progression from normoglycemia to diabetes (DM) as a competing event in the progression from normoglycemia to pre-DM. Subgroup analyses and multiple sensitivity analyses were also performed to ensure the robustness of the findings.
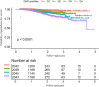
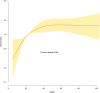
Results: Following multivariate adjustment, elevated GHR demonstrated a significant correlation with increased risk of progression from normoglycemia to pre-DM, showing a hazard ratio(HR) of 1.061 (95% CI: 1.028-1.095) for each 5-unit increment. A nonlinear relationship between them was identified, with an inflection point at a GHR value of 24.37. On the left side of the inflection point, the HR for the association between GHR (per 5-unit increase) and pre-DM risk was 1.394 (95% CI: 1.197, 1.623). Furthermore, the competing risk model revealed an HR of 1.05 (95% CI: 1.02, 1.09) for the association between GHR (per 5-unit increase) and pre-DM risk. Multiple sensitivity analyses confirmed the stability and reliability of these results.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that elevated GHR exhibits both a positive and nonlinear relationship with the risk of progression from normoglycemia to pre-DM among Chinese adults. Maintaining GHR values below the threshold of 24.37, coupled with further reduction efforts, may serve as an effective strategy to minimize pre-DM risk.
Keywords: competing risk model; nonlinearity; prediabetes; γ-glutamyl transferase; γ-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein ratio.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Yu, Shi, Liu, Li and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ebrahimi H, Aryan Z, Saeedi Moghaddam S, Bisignano C, Rezaei S, Pishgar F, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1923–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

