Dumbbell versus cable lateral raises for lateral deltoid hypertrophy: an experimental study
- PMID: 40692697
- PMCID: PMC12277279
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1611468
Dumbbell versus cable lateral raises for lateral deltoid hypertrophy: an experimental study
Abstract
Introduction: This study compared the effects of dumbbell versus cable lateral raises on lateral deltoid muscle thickness (MT) in resistance-trained men and women, with shoulder adduction/abduction range of motion standardised and matched between conditions.
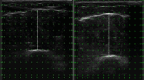
Methods: Twenty-four participants completed an eightweek intervention comprising two weekly resistance training sessions of five sets of lateral raises completed to momentary failure. The study employed a within-participant design with each participant's arms randomly allocated to the cable or dumbbell lateral raise. MT of the proximal and distal lateral deltoid was assessed via B-mode ultrasound. Data were analysed in a Bayesian framework including both univariate and multivariate mixed effect models with random effects. Differences between conditions were estimated as average treatment effects, with inferences based on posterior distributions and Bayes Factors (BFs).
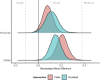
Results: Results showed that lateral deltoid muscle thickness increased by 3.3%-4.6% during the intervention. Moreover, univariate analyses provided "moderate" support for the null hypothesis for both the distal (BF = 0.27) and proximal (BF = 0.22) lateral deltoid. Multivariate analysis provided "extreme" support for the null hypothesis (BF < 0.01). Within-intervention results indicated that conditions produced small or small to medium improvements based on resistance training specific thresholds.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our data suggest that both dumbbell and cable lateral raises are similarly effective for increasing lateral deltoid muscle hypertrophy in resistance-trained lifters.
Keywords: Length-tension relationship; muscle thickness; resistance profile; shoulder; within-participant design.
Copyright © 2025 Larsen, Wolf, Schoenfeld, Sandberg, Fredriksen, Kristiansen, van den Tillaar, Swinton and Falch.
Conflict of interest statement
BJS formerly served on the scientific advisory board for Tonal Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Botton C. E., Wilhelm E. N., Ughini C. C., Pinto R. S., Lima C. S. (2013). Electromyographical analysis of the deltoid between different strength training exercises. Med. Sport, 17 (2). 10.5604/17342260.1055261 - DOI
-
- Bürkner P.-C. (2017). Brms: an R package for Bayesian multilevel models using stan. J. Stat. Softw. 80, 1–28. 10.18637/jss.v080.i01 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

