Identification of a novel microdeletion at 9q21.13 in a family with epilepsy, intellectual disability, and speech disorders and literature review
- PMID: 40692708
- PMCID: PMC12277573
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1616005
Identification of a novel microdeletion at 9q21.13 in a family with epilepsy, intellectual disability, and speech disorders and literature review
Abstract
Background: At present, there are few reports on 9q21.13 microdeletion syndrome, which is characterized by intellectual disability, epilepsy, autistic behaviour, and recognizable facial features, etc. The aim of this study is to enrich the phenotypic features of 9q21.13 microdeletion syndrome and expand the possible segments of 9q21.13 microdeletion syndrome.
Methods: Four individuals from a 3-generation Chinese family with epilepsy, intellectual disability, and speech disorders were recruited in this study. Whole exome sequencing (WES) and chromosome microarray analysis (CMA) techniques were used for genetic testing. The pathogenicity of CNVs was interpreted following the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) standards and guidelines.
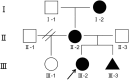
Results: A 9q21.13 microdeletion with a fragment size of approximately 2.35 Mb was identified in the proband, the proband's mother and grandmother and even the fetus. And this region encompasses 6 protein coding genes, namely, ALDH1A1, ANXA1, GDA, RORB, TMC1, and ZFAND5.
Conclusion: In this article, we report a girl with epilepsy, intellectual disability, speech disorders, delayed motor development, and autism. We identified a novel 9q21.13 microdeletion with a fragment size of approximately 2.35 Mb in 4 individuals from a 3-generation Chinese family by WES and CMA techniques. Within the region, the RORB gene is a strong candidate gene for complex neurodevelopmental disorders. Herein, we speculate that RORB makes a significant contribution to the clinical phenotypes caused by 9q21.13 microdeletion.
Keywords: 9q21.13 microdeletion; chromosome microarray analysis; copy number variations; epilepsy; intellectual disability; whole exome sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Li, Han, Hou, Wei and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Non-speech oral motor treatment for children with developmental speech sound disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 25;2015(3):CD009383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25805060 Free PMC article.
-
All-Cause Mortality and Specific Causes of Death in Autism: A Nationwide Analysis.Autism Adulthood. 2025 Feb 5;7(1):81-92. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0103. eCollection 2025 Feb. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40151655
-
[Genetic analysis for a pedigree with Structural heart defects and renal anomalies syndrome caused by variants of TMEM260 gene].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Apr 10;42(4):460-468. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20241023-00552. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40555660 Chinese.
-
TET3-Related Beck-Fahrner Syndrome.2023 May 18. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2023 May 18. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 37200470 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- André E., Conquet F., Steinmayr M., Stratton S. C., Porciatti V., Becker-André M. (1998). Disruption of retinoid-related orphan receptor beta changes circadian behavior, causes retinal degeneration and leads to vacillans phenotype in mice. EMBO J. 17 (14), 3867–3877. 10.1093/emboj/17.14.3867 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartnik M., Szczepanik E., Derwińska K., Wiśniowiecka-Kowalnik B., Gambin T., Sykulski M., et al. (2012). Application of array comparative genomic hybridization in 102 patients with epilepsy and additional neurodevelopmental disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 159b (7), 760–771. 10.1002/ajmg.b.32081 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boudry-Labis E., Demeer B., Le Caignec C., Isidor B., Mathieu-Dramard M., Plessis G., et al. (2013). A novel microdeletion syndrome at 9q21.13 characterised by mental retardation, speech delay, epilepsy and characteristic facial features. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 56 (3), 163–170. 10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.12.006 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

