Sustainable synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Persicaria lapathifolia: versatile anticancer and antibacterial applications
- PMID: 40692720
- PMCID: PMC12277169
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1601811
Sustainable synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Persicaria lapathifolia: versatile anticancer and antibacterial applications
Abstract
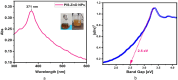
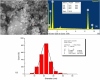
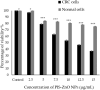
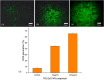
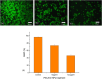
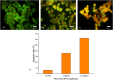
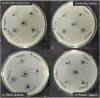
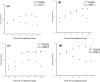
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers in the world and one of the leading causes of cancer mortality. In this study, zinc oxide nanoparticles (PlS-ZnO NPs) were synthesized eco-friendly using an aqueous extract from the stems of Persicaria lapathifolia and their anticancer and antibacterial activities were evaluated. The PlS-ZnO NPs were prepared by a simple sol-gel combustion method and investigated by different spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. The resulting nanoparticles were of polygonal and hexagonal morphology with the average size of 21.45 nm. The PlS-ZnO NPs exhibited high cytotoxicity against human colorectal cancer cell line (HCT-116) with IC50 value of 11.31 μg/mL. Cytomorphological studies showed that these nanoparticles killed cells through both apoptosis and necrosis. Apoptotic process was accompanied by enhancement of intracellular ROS and MMP. Moreover, the PlS-ZnO NPs exhibited excellent antibacterial activity towards different pathogenic bacteria like Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium, Vibrio cholerae and Proteus vulgaris and was found to be better than the positive control amoxicillin. These results indicate that the green synthesized PlS-ZnO NPs can be considered as a potential multifunctional agent for the treatment of colorectal cancer and bacterial infections. The environmentally friendly and cost-effective synthesis of PlS-ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) utilizing P. lapathifolia enhances the potential of this nanomaterial for medical applications. This sustainable approach not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with the increasing demand for biocompatible materials in healthcare.
Keywords: Persicaria lapathifolia; ROS; antibacterial activity; apoptosis; colorectal cancer; green synthesis; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2025 Sholkamy, Abdelhamid, Rebai, Sivapunniyam, Ki, Pack and Khalifa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Eco-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Siirt pistachio thin shell extract: promising applications in photocatalysis and antibacterial solutions.Int J Phytoremediation. 2025 Jul 9:1-13. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2025.2530018. Online ahead of print. Int J Phytoremediation. 2025. PMID: 40635233
-
Biological activities of optimized biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Proteus mirabilis PQ350419 alone or combined with chitosan and ampicillin against common multidrug-resistant bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jul 5;24(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02783-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40618114 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological properties of Bergenia ciliata synthesized green zinc sulfide nanoparticles (ZnS-NPs) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs).Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025 Aug 25. doi: 10.1007/s00449-025-03225-2. Online ahead of print. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025. PMID: 40855027
-
Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5454. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125454. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Abd El-Hafeez A. A., Khalifa H. O., Elgawish R. A., Shouman S. A., Abd El-Twab M. H., Kawamoto S. (2018). Melilotus indicus extract induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via a mechanism involving mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cytotechnology 70 (4), 831–842. 10.1007/s10616-018-0195-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adjei I. M., Sharma B., Labhasetwar V. (2014). Nanoparticles: cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Nanomaterial: impacts on cell biology and medicine, 73–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

