Association of the expression of 5-FU biomarkers with aging and prognosis in elderly patients with lung cancer treated with S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy: Follow-up results of the Setouchi Lung Cancer Group Study 1201
- PMID: 40692744
- PMCID: PMC12278714
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2025.2874
Association of the expression of 5-FU biomarkers with aging and prognosis in elderly patients with lung cancer treated with S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy: Follow-up results of the Setouchi Lung Cancer Group Study 1201
Abstract
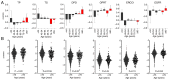
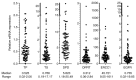
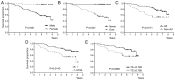
Managing elderly patients presents several challenges because of age-related declines; however, age should not be the sole determinant for adjuvant treatment decisions in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Moreover, age may affect the expression of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) biomarkers. The present study assessed: i) The effect of age on the expression levels of 5-FU biomarkers by analyzing a public database; and ii) the ability of these biomarkers to predict clinical outcomes in elderly patients with NSCLC who underwent complete resection in the Setouchi Lung Cancer Group Study 1201 (SCLG1201) followed by S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy. Changes in gene expression levels across age groups were assessed by analyzing The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The expression of 5-FU biomarkers, including thymidylate synthase (TS), dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), orotate phosphoribosyltransferase, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1), were assessed via quantitative reverse-transcription PCR assays in 89 elderly patients (≥75 years) with NSCLC who received adjuvant chemotherapy with oral fluoropyrimidine prodrug S-1 in the SLCG1201 trial. TCGA database analysis (n=955) showed that TS expression decreased significantly with aging, especially in the age group ≥75. In the SCLG1201 trial, univariate analysis revealed that EGFR upregulation and TS downregulation were correlated with favorable recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), respectively. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that pathological stage was an independent prognostic factor for both RFS and OS. EGFR mutations were associated with upregulation of DPD and EGFR, and downregulation of TS and ERCC1. In conclusion, although pathological stage is an independent prognostic factor for survival, EGFR upregulation and TS downregulation may be a greater predictor of clinical outcomes in elderly patients with NSCLC treated with S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy. The age-related decrease in TS expression supports the potential benefit of 5-FU therapies in elderly patients. Nonetheless, further research is warranted to validate these results.
Keywords: DPD; EGFR; ERCC1; OPRT; S-1; TP; TS; adjuvant chemotherapy; elderly patients; non-small cell lung cancer.
Copyright: © 2025 Soh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pallis AG, Gridelli C, Wedding U, Faivre-Finn C, Veronesi G, Jaklitsch M, Luciani A, O'Brien M. Management of elderly patients with NSCLC; updated expert's opinion paper: EORTC elderly task force, lung cancer group and international society for geriatric oncology. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1270–1283. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shirasaka T, Shimamato Y, Ohshimo H, Yamaguchi M, Kato T, Yonekura K, Fukushima M. Development of a novel form of an oral 5-fluorouracil derivative (S-1) directed to the potentiation of the tumor selective cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil by two biochemical modulators. Anticancer Drugs. 1996;7:548–557. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199607000-00010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama O, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Takada K, Baba K, Saito H, Sugino Y, Yamamoto M, Ogasawara T, Kondo M, et al. Phase II study of S-1 monotherapy as a first-line treatment for elderly patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: The Central Japan lung study group trial 0404. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22:811–816. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283440231. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shiroyama T, Kijima T, Komuta K, Yamamoto S, Minami S, Ogata Y, Okafuji K, Imamura F, Hirashima T, Tachibana I, et al. Phase II tailored S-1 regimen study of first-line chemotherapy in elderly patients with advanced and recurrent non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012;70:783–789. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-1958-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
