Clinical and therapeutic insights into intraventricular metastases from extracranial solid tumors: Patterns, prognosis and management
- PMID: 40692746
- PMCID: PMC12278710
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2025.2875
Clinical and therapeutic insights into intraventricular metastases from extracranial solid tumors: Patterns, prognosis and management
Abstract
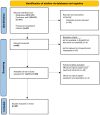
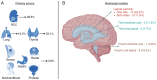
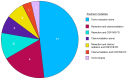
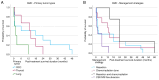
Solid intraventricular metastasis from extracranial primary tumors (SIMs) are rare and their diagnosis and management remain poorly understood. A systematic review was conducted using the MEDLINE and Embase databases to identify relevant studies published until November 2024. Data such as presenting symptoms, treatments and survival outcomes were extracted from included articles on patients with SIMs. A total of 26 studies, involving 26 patients (34.6% female patients; median age, 64 years), met the inclusion criteria. The most common primary tumor was renal cell carcinoma (38.5%). Furthermore, 57.7% of patients had metastasis to one or both lateral ventricles, 19.2% had metastasis to the lateral and fourth ventricle, 11.5% had metastasis to the third ventricle alone, 7.7% had metastasis to the lateral and third ventricle, and 3.8% had metastasis to the fourth ventricle alone. Treatment approaches varied, with tumor resection (42.3%) being the most common intervention, followed by tumor resection with adjuvant chemo/radiation therapy (15.4%). The median post-treatment survival time was 4.3 months. Patients receiving tumor resection combined with radiation or chemotherapy had the longest survival (median, 24 months), compared with those undergoing tumor resection alone (median, 2 months). SIMs are rare but clinically significant, with variable treatment approaches and survival outcomes. Multimodal therapy offers the best prognosis, although survival remains generally poor. Further research is needed to better understand the pathophysiology, treatment strategies and outcomes of SIMs.
Keywords: choroid plexus; intraventricular; management; metastases; multimodal treatment.
Copyright: © 2025 Arunachalam Sakthiyendran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
