The effect of abaloparatide on the proximal femur in men with osteoporosis assessed by three-dimensional dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
- PMID: 40692760
- PMCID: PMC12278270
- DOI: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziaf098
The effect of abaloparatide on the proximal femur in men with osteoporosis assessed by three-dimensional dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Abstract
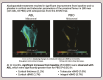
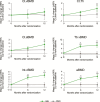
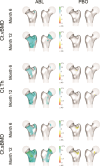
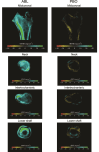
Abaloparatide treatment significantly increased BMD at the LS, TH, and FN compared with placebo in men with osteoporosis in the phase 3 ATOM trial. The current study used 3D-DXA modeling to evaluate the effects of abaloparatide on cortical and trabecular compartments of the proximal femur in ATOM study participants. Proximal femur DXA images were retrospectively analyzed using 3D-DXA (3D-Shaper software v2.12.0, 3D-Shaper Medical, Barcelona, Spain) to evaluate changes in bone parameters from baseline at months 6 and 12 in all randomized men from the ATOM trial. Between-group comparisons were made for percent change from baseline data based on a mixed-effect repeated-measure model with treatment, visit, treatment-by-visit interaction, and type of DXA scanner as fixed effects. Other covariates include BMI, age, and baseline values of bone parameters. Abaloparatide treatment significantly increased integral volumetric BMD (vBMD) (3.7%), trabecular vBMD (7.0%), cortical thickness (1.1%), and cortical surface BMD (1.7%) at 12 mo compared to baseline (p < .0001). Changes were greater for abaloparatide compared to placebo for all 4 parameters (p < .01). Significant increases from baseline compared to placebo in integral vBMD (2.7% vs -0.1%, p < .0001) and trabecular vBMD (6.1% vs -0.6%, p < .0001) were also observed at 6 mo. In conclusion, in men with osteoporosis, abaloparatide improved proximal femur 3D-DXA parameters broadly consistent with results in postmenopausal women in the ACTIVE study, adding to the growing data on abaloparatide bone structure effects at the hip.
Keywords: 3D modeling; DXA; abaloparatide; cortical volumetric BMD; osteoporosis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Conflict of interest statement
R.D. reports research support (to institution) from Alexion, Radius Health, Inc. (Radius), Shire, and Takeda, and consultant or scientific advisory board roles for Alexion, Amgen, Ascendis, Ultragenyx, Radius, and Kyowa Kirin. J.B. and Y.W. are employees of Radius. B.H.M. is a former employee of Radius. L.H. is an employee and shareholder of 3D-Shaper Medical, which received funding for this study from Radius. N.B. reports research support (to institution) from Radius.
Figures
Similar articles
-
3D-DXA reveals significant effects of burosumab on trabecular and cortical skeletal envelopes in symptomatic adults with X-linked Hypophosphatemia.J Bone Miner Res. 2025 Jul 13:zjaf092. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjaf092. Online ahead of print. J Bone Miner Res. 2025. PMID: 40652299
-
Bone turnover markers predict changes in bone mineral density in men treated with abaloparatide: results from the abaloparatide for the treatment of men with osteoporosis (ATOM) study.J Bone Miner Res. 2025 Mar 15;40(3):315-322. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjaf003. J Bone Miner Res. 2025. PMID: 39791502 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Positive Effect of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Consumption on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Assessed by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Based 3-Dimensional Modeling.J Bone Metab. 2025 May;32(2):123-132. doi: 10.11005/jbm.24.827. Epub 2025 May 31. J Bone Metab. 2025. PMID: 40537107 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment for osteoporosis in people with beta-thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 9;5(5):CD010429. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010429.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37159055 Free PMC article.
-
The Safety and Efficacy of Abaloparatide on Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Ther. 2024 Mar;46(3):267-274. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.12.010. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Clin Ther. 2024. PMID: 38307725
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

