Yuanhuacine modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 through regulation of the JAK1/STAT3 pathway and prevents tubular damage in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 40692765
- PMCID: PMC12277938
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2025.12918
Yuanhuacine modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 through regulation of the JAK1/STAT3 pathway and prevents tubular damage in acute kidney injury
Abstract
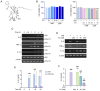
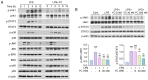
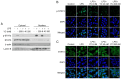
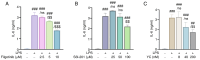
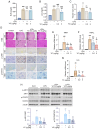
Inflammation is an immune response that activates immune cells to protect the host from infection or tissue damage; however, excessive inflammation can lead to sepsis and acute kidney injury (AKI). Yuanhuacine (YC), a physiologically active compound derived from Daphne genkwa flowers, has demonstrated its therapeutic potential in various diseases, including inflammatory diseases and cancer. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms by which YC regulates inflammatory cytokines and exerts efficacy against AKI remain to be elucidated. The present study aimed to investigate the role of YC in regulating cytokines in human macrophages and to evaluate its protective effect in a mouse model of AKI. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to stimulate THP-1 macrophages in vitro, and LPS was administered intraperitoneally to establish an in vivo AKI model. LPS treatment significantly increased interleukin 6 (IL-6) expression in both macrophages and in mice with AKI. However, YC treatment effectively reduced IL-6 production by inhibiting the activation of Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in macrophages, and YC was confirmed to inhibit LPS-induced tubular damage in the mouse model of AKI. In conclusion, YC may serve as a potential therapeutic agent in the prevention of AKI and other IL-6-related inflammatory diseases by promoting JAK1/STAT3 dephosphorylation to facilitate inflammation resolution.
Keywords: AKI; IL-6; JAK1/STAT3 pathway; LPS; YC.
Copyright: © 2025 Park and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
