Comparison of IgG4 with inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6 and TNFα) in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40692774
- PMCID: PMC12277376
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1607074
Comparison of IgG4 with inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6 and TNFα) in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic joint inflammation driven by a complex interplay of autoantibodies, cytokines, and chemokines. While the role of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1(IL-1), interleukin-6(IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), in the pathogenesis of RA has been well-established, the contribution of the immunoglobulin G subclass IgG4 remains a topic of ongoing investigation. This cross sectional study aim was to compare the levels of IgG4 and these key inflammatory cytokines in Malaysian patients with RA.
Methods: The study enrolled a total of 194 RA patients. All subjects were tested for their serum IgG4, IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α levels. Besides, subjects were assessed for their disease activity based on DAS28, functional disability based on HAQ-DI (Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index) and the severity of the radiographic joint erosions by using the Modified Sharp Score (MSS).
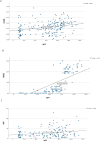
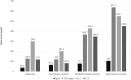
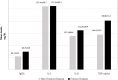
Results: Correlation analysis revealed a moderate positive association between IgG4 and IL-6 levels (r=0.348, p=0.001), but there were no significant correlations with IL-1 and TNFα levels. IgG4 levels showed a significant positive correlation with DAS28, MSS, and HAQ-DI. All 3 cytokine levels had significant relationships with the DAS28 scores, but for the MSS, only TNF-α (p=0.024) and IL-6 (p=0.016) demonstrated significant associations. None of the cytokines correlated significantly with the HAQ-DI scores.
Conclusion: The positive correlation between IgG4 and IL-6 levels underscores the possibility for IL-6-driven pathways to influence IgG4 production. Serum IgG4 was associated with more clinical aspects of RA compared to the classical inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: cytokine; disease activity; immunoglobulin G; joint erosions; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Sakthiswary, Shaharir, Abdul Wahab and Uma Rajeswaran.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
-
Relationship between serum vitamin D levels and pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis combined with cardiovascular disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul 26. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07587-6. Online ahead of print. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40715933
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical