Influences of metabolism and lipid homeostasis on regulatory vs. conventional T cells and implications for autoimmunity
- PMID: 40692789
- PMCID: PMC12277389
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613230
Influences of metabolism and lipid homeostasis on regulatory vs. conventional T cells and implications for autoimmunity
Abstract
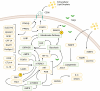
Regulatory T cells are essential for suppressing an overactive immune system, especially concerning autoimmune disease, tumor growth, and inflammatory disease. This suppressive nature of regulatory T cells is largely due to their metabolic profiles determined by metabolic reprogramming upon activation and subsequent differentiation. As regulatory T cells tend to process and cycle energy differently from other T cell subsets, we are interested in what metabolic processes support regulatory T cell function. This review will consider how regulatory T cells compare with conventional T cells in terms of their participation in distinct metabolic pathways and how the presence of regulatory T cell-specific molecules influences proliferation and suppressive function. Additionally, this review will identify possible metabolic targets of regulatory T cells that could be targeted for development of autoimmune disease therapies.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; lipid metabolism; mTOR; metabolic reprograming; mevalonate (MVA) pathway; regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2025 Nguyen, Lee and Walsh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

