Cathepsin S: molecular mechanisms in inflammatory and immunological processes
- PMID: 40692794
- PMCID: PMC12277131
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1600206
Cathepsin S: molecular mechanisms in inflammatory and immunological processes
Abstract
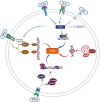
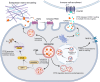
Cathepsin S (CTSS), a lysosomal cysteine protease predominantly expressed in immune cells, governs inflammatory and immunological cascades through proteolytic activity. Beyond maintaining lysosomal proteostasis through protein degradation, CTSS executes dual immunomodulatory functions: intracellularly processing antigen-presenting molecules and modulating inflammatory signaling cascades; extracellularly activating protease-activated receptors (PARs) and remodeling the extracellular matrix (ECM). Its dysregulation drives pathology in autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammation, and neoplasia, establishing CTSS as a multifaceted therapeutic target. This review comprehensively explores the contributions of CTSS signaling in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, critically evaluates its therapeutic potential, highlighting its significance in the development of innovative treatment strategies.
Keywords: cathepsin S (CTSS); immunoregulation; inflammatory disease; molecular mechanism; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Zhang, Deng and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The multiple functions of CD5 in diseases related to immune disorders.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2519682. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2519682. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40539686 Review.
-
Cathepsin S: investigating an old player in lung disease pathogenesis, comorbidities, and potential therapeutics.Respir Res. 2020 May 12;21(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01381-5. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32398133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular cathepsin S and intracellular caspase 1 activation are surrogate biomarkers of particulate-induced lysosomal disruption in macrophages.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016 Apr 23;13:19. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0129-5. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27108091 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting cathepsin S in pulmonary fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jan;145:112245. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112245. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34772578 Review.
-
Anti-atherogenic immune checkpoint TIM-3 as a promising pharmacologic target toward ischemic heart diseases: a prospective review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 23;52(1):623. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10729-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40549173 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

