Association of Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Grade With 28-Day All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Retrospective Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database
- PMID: 40692980
- PMCID: PMC12279418
- DOI: 10.1155/mi/9930648
Association of Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Grade With 28-Day All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Retrospective Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database
Abstract
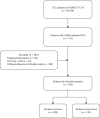
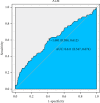
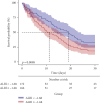
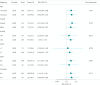
The albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade, a validated prognostic tool in cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma, has not been evaluated in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This retrospective cohort study, utilizing data from the MIMIC-IV (v3.0) database, aimed to assess ALBI's predictive value for 28-day all-cause mortality in 338 adult ARDS patients admitted to the ICU. Patients were stratified into survivors (209 cases) and nonsurvivors (129 cases), with a 28-day mortality rate of 38.2%. Multivariable Cox regression identified ALBI as an independent predictor of 28-day mortality (HR = 1.46, 95% CI: 1.09-1.95, p=0.011). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 61.1% (95% CI: 54.7%-67.4%) with an optimal ALBI cutoff of -1.681; Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves confirmed significantly higher mortality in patients with ALBI ≥-1.681 versus ALBI <-1.681 (p=0.0098). Subgroup analyses revealed no significant interactions between ALBI and clinical variables (interaction p: 0.672-0.85). These findings demonstrate ALBI's utility as a novel, independent prognostic marker for short-term mortality risk in ARDS patients.
Keywords: 28 days; acute respiratory distress syndrome; albumin-bilirubin; all-cause mortality; cohort; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 Weixiao Chen et al. Mediators of Inflammation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NHANES 2005-2018 data reveal high albumin-bilirubin scores are associated with depression.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-07082-x. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40597971 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Albumin Corrected Anion Gap and 28-Day All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Failure in ICU: A Retrospective Study Based on the MIMIC-IV Database.Clin Respir J. 2025 Jul;19(7):e70100. doi: 10.1111/crj.70100. Clin Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40631543 Free PMC article.
-
Association between international normalized ratio-to-albumin ratio and mortality in critically ill patients with gastrointestinal bleeding: a retrospective MIMIC-IV database study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 11;25(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04179-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40790158 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of Albumin Bilirubin Grade as a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2023 Jun;54(2):420-432. doi: 10.1007/s12029-022-00832-0. Epub 2022 May 30. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2023. PMID: 35635637
-
Partial liquid ventilation for preventing death and morbidity in adults with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 23;2013(7):CD003707. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003707.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23881653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri V. M., Rubenfeld G. D., et al. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA . 2012;307:2526–2533. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

