Vagally mediated heart rate variability modulates the association between the perceived workload and the Stroop effect on behavioral performance
- PMID: 40693346
- PMCID: PMC12280812
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70466
Vagally mediated heart rate variability modulates the association between the perceived workload and the Stroop effect on behavioral performance
Abstract
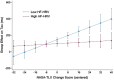
Vagally mediated heart rate variability (vmHRV) reflects top-down cognitive processes involved in emotion-cognition integration. Using cognitive control can be effortful and increase negative affect. However, this intrinsic affective component of cognitive control has not been well studied, and the role of vmHRV in the association between subjective experience in using cognitive control and behavioral performance remains unknown. The current study aimed to examine the relationship of vmHRV with cognitive control and perceived workload in a cognitive task. Eighty-one participants performed the Stroop interference task. Participants rated subjective workload using the NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX) scale for congruent and incongruent trials separately. Moreover, cognitive performance was analyzed with the ex-Gaussian model, from which the parameters μ and τ were derived to reflect sensorimotor processing and inhibitory control, respectively. Multiple regressions were used to analyze the effects of TLX change score (incongruent-congruent), vmHRV, and their interaction on the Stroop effect. Results showed that vmHRV negatively predicted the Stroop effect on τ. Importantly, vmHRV moderated the association between perceived workload and the Stroop effect on τ. Our findings highlight the role of cardiac vagal control in emotion-cognition integration and have theoretical and practical implications.
Keywords: ex‐Gaussian parameters; inhibitory control; stroop effect; vagally mediated heart rate variability; workload.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aiken, L. S. , West, S. G. , & Reno, R. R. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage.
-
- Alaimo, A. , Esposito, A. , Orlando, C. , & Simoncini, A. (2020). Aircraft pilots workload analysis: Heart rate variability objective measures and NASA‐task load index subjective evaluation. Aerospace, 7(9), 137. 10.3390/aerospace7090137 - DOI
-
- Alam, S. , Revi, G. S. , Kerick, S. E. , Yang, X. , Robucci, R. , Banerjee, N. , & Spangler, D. P. (2023). Anticipatory cardiac deceleration estimates cognitive performance in virtual reality beyond tonic heart period and heart period variability. Biological Psychology, 181, 108602. 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2023.108602 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

