Balancing reaction-diffusion network for cell polarization pattern with stability and asymmetry
- PMID: 40693535
- PMCID: PMC12283076
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.96421
Balancing reaction-diffusion network for cell polarization pattern with stability and asymmetry
Abstract
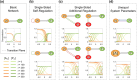
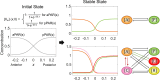
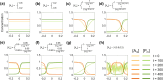
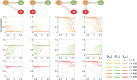
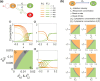
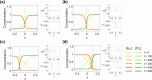
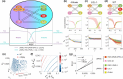
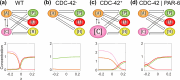
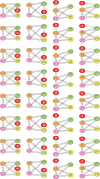
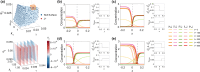
Cell polarization is a critical process that separates molecular species into two distinct regions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, guiding biological processes such as cell division and cell differentiation. Although several underlying antagonistic reaction-diffusion networks capable of setting up cell polarization have been identified experimentally and theoretically, our understanding of how to manipulate pattern stability and asymmetry remains incomplete, especially when only a subset of network components is known. Here, we present numerical results to show that the polarized pattern of an antagonistic 2-node network collapses into a homogeneous state when subjected to single-sided self-regulation, single-sided additional regulation, or unequal system parameters. However, polarity restoration can be achieved by combining two modifications with opposing effects. Additionally, spatially inhomogeneous parameters favoring respective domains stabilize their interface at designated locations. To connect our findings to cell polarity studies of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans zygote, we reconstituted a 5-node network where a 4-node circuit with full mutual inhibitions between anterior and posterior is modified by a mutual activation in the anterior and an additional mutual inhibition between the anterior and posterior. Once again, a generic set of kinetic parameters moves the interface towards either the anterior or posterior end, yet a polarized pattern can be stabilized through tuning of one or more parameters coupled to intracellular or extracellular spatial cues. A user-friendly software, PolarSim, is constructed to facilitate the exploration of networks with alternative node numbers, parameter values, and regulatory pathways.
Keywords: C. elegans; Caenorhabditis elegans; asymmetry; cell polarization; computational biology; embryogenesis; physics of living systems; reaction-diffusion network; stability; systems biology.
© 2024, Chen, Guan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YC, GG, LT, CT No competing interests declared
Figures











Update of
- doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2401.07227
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96421.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96421.2
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

