Glycemic Control and Prostate Cancer Mortality Risk in Veterans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 40693585
- PMCID: PMC12314478
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-25-0037
Glycemic Control and Prostate Cancer Mortality Risk in Veterans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
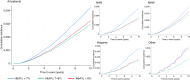
This retrospective cohort study of veterans diagnosed with diabetes mellitus evaluated the association between time-varying measures of glycemic control and the time to prostate cancer-specific mortality. Competing risk Cox regression models were developed to estimate the association of glycemic control and prostate cancer mortality for the entire sample and stratified by racial and ethnic groups. A total of 763,424 veterans with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were included. In the fully adjusted models, moderate glycemic control [hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 7%-8%] was associated with a 23% (HR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.85) lower risk and poor glycemic control (HbA1c >8%) was associated with a 15% (HR, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.99) lower risk of prostate cancer mortality compared with good glycemic control (HbA1c <7%), respectively. In the analyses stratified by race and ethnicity, moderate glycemic control was associated with a lower risk of prostate cancer mortality in non-Hispanic White and non-Hispanic Black veterans.
Significance: Unlike many other cancers, there is an inverse association between prostate cancer risk and T2DM diagnosis. In this large, retrospective study of male veterans with T2DM, we observed an inverse association between glycemic control and prostate cancer mortality. Further research is required to verify this relationship in prospective studies and identify the potential mechanisms contributing to these findings.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Gebregziabher reports grants from VA Health Services and Development during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures


References
-
- (CDC) CfDCaP . National diabetes statistics report. 2024[cited 2024 Dec 11]. Available from:https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html.
-
- (CSPEAR) VCSPEAR . Type 2 diabetes mellitus. 2020.
-
- Safadi H, Balogh Á, Lám J, Nagy A, Belicza É. Associations between diabetes and cancer: a 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024;211:111665. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

