Analysis of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis gene transcripts during experimental primate necrotizing myositis
- PMID: 40693777
- PMCID: PMC12345147
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01349-25
Analysis of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis gene transcripts during experimental primate necrotizing myositis
Abstract
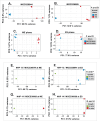
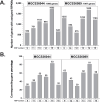
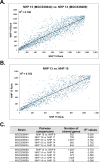
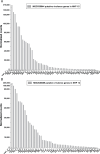
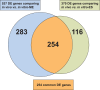
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis (SDSE) is a gram-positive bacterial pathogen capable of causing various infections in humans. Recently, isolates of SDSE emm type stG62647 have emerged as a cause of severe invasive infections, including necrotizing myositis. However, the molecular processes underlying these infections remain poorly understood. To address this gap, we performed RNAseq analysis to examine SDSE gene transcript levels during experimental necrotizing myositis infection in non-human primates, animals phylogenetically closely related to humans. We analyzed the transcriptomes of two related SDSE stG62647 human isolates (MGCS36044 and MGCS36089) during necrotizing myositis infection in six non-human primates. The transcriptome from in vitro growth in nutrient-rich media differed considerably from that of SDSE bacteria grown in vivo in experimental necrotizing myositis, with 254 genes differentially expressed, indicating extensive genetic adaptation in infected skeletal muscle. Notably, we observed a marked upregulation of ihk-irr genes encoding a two-component regulatory system that promotes evasion of phagocytosis and resistance to killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in Streptococcus pyogenes. Similarly, genes comprising the sag operon encoding the streptolysin S cytolytic toxin virulence factor demonstrated very high transcript abundance in vivo. Additionally, we present evidence that a 40-nt deletion in fasB alters expression of ska, encoding streptokinase. Collectively, our data provide new insights into the SDSE genes transcribed in vivo, thereby enhancing our understanding of the molecular basis of pathogen and primate host interactions. The SDSE genes identified in this study offer promising targets for future studies on molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions.IMPORTANCEStreptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis (SDSE) has emerged as an increasingly important bacterial pathogen causing serious invasive infections in humans worldwide. Despite its clinical importance, the mechanisms through which SDSE causes infections remain poorly understood, and no licensed vaccine currently exists. SDSE can cause necrotizing myositis, an infection with high morbidity and mortality. We used a primate infection model and bacterial transcriptome analysis to gain new understanding of the molecular events contributing to SDSE pathogenesis in necrotizing myositis. Our results provide extensive new information about the transcriptome of SDSE in vivo and reveal numerous potential targets for future therapeutic and vaccine research.
Keywords: RNAseq; Streptococcus dysgalactiae; emerging clone; pathogenesis; primate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrative genomic, virulence, and transcriptomic analysis of emergent Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis (SDSE) emm type stG62647 isolates causing human infections.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0257824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02578-24. Epub 2024 Oct 17. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39417630 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Ophthalmia Neonatorum.2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31855399 Free Books & Documents.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Kaci A, Jonassen CM, Skrede S, Sivertsen A, Steinbakk M, Oppegaard O, Norwegian Study Group on Streptococcus dysgalactiae . 2023. Genomic epidemiology of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis strains causing invasive disease in Norway during 2018. Front Microbiol 14:1171913. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1171913 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leitner E, Zollner-Schwetz I, Zarfel G, Masoud-Landgraf L, Gehrer M, Wagner-Eibel U, Grisold AJ, Feierl G. 2015. Prevalence of emm types and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Austria. Int J Med Microbiol 305:918–924. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2015.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
