Breaking down biofilms across critical priority fungal pathogens: proteomics and computational innovation for mechanistic insights and new target discovery
- PMID: 40693795
- PMCID: PMC12345193
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02303-24
Breaking down biofilms across critical priority fungal pathogens: proteomics and computational innovation for mechanistic insights and new target discovery
Abstract
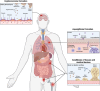
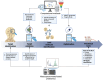
Fungal biofilms are complex microbial structures associated with persistent and progressive infections, such as cryptococcal meningitis, invasive aspergillosis, and invasive candidiasis, leading to thousands of deaths annually. The prevalence of fungal biofilm formation during infections, with its heightened resistance to antifungal drugs, highlights the urgency for the discovery and development of new antifungals with antibiofilm activity. Current advances in mass spectrometry-based proteomics and computational platforms provide a powerful toolkit to accelerate drug discovery from target identification to optimization of a lead molecule. In this review, we highlight fungal biofilms of four critical priority fungal pathogens (as deemed by the World Health Organization) and define important technological considerations for proteomics and computational methodologies. Additionally, we explore recent proteomics and computational applications within fungal biofilms for the identification and elucidation of biological mechanisms underscoring biofilm formation as well as the discovery of novel putative antibiofilm targets.
Keywords: biofilms; computational methods; critical priority fungal pathogens; drug discovery; mass spectrometry-based proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of recombinant 1,3-β-glucanase as antibiofilm to prevent antimicrobial resistance in antifungal therapy for vulvovaginitis candidiasis.Open Vet J. 2025 May;15(5):2182-2192. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i5.36. Epub 2025 May 31. Open Vet J. 2025. PMID: 40557080 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase activity in fungal pathogens compromise thermal tolerance pathways.mBio. 2025 Aug 25:e0179525. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01795-25. Online ahead of print. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40852984
-
Inhibitors of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase activity in fungal pathogens compromise thermal tolerance pathways.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 18:2025.03.07.642065. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.07.642065. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40370958 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Antifungal agents for preventing fungal infections in non-neutropenic critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 16;2016(1):CD004920. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004920.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26772902 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment for HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 25;7(7):CD005647. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005647.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30045416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2024. World malaria report 2024: addressing inequity in the global malaria response. World Health Organization, Geneva
-
- World Health Organization . 2024. Global tuberculosis report 2024. World Health Organization, Geneva
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
