Puerarin attenuates S. aureus-induced mastitis through inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis by activating the SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40693808
- PMCID: PMC12403620
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02859-24
Puerarin attenuates S. aureus-induced mastitis through inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis by activating the SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway
Abstract
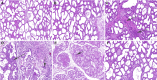
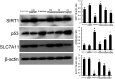
Mastitis, one of the most prevalent diseases in humans and animals, is commonly caused by local infection of the mammary gland. Puerarin inhibits mitochondrial oxidative stress and acute liver injury in mice. However, the therapeutic effect of puerarin on Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis is still not well understood. This study was designed to investigate the therapeutic role and mechanism of puerarin on S. aureus-induced mastitis. S. aureus was injected through the mammary gland to induce mouse mastitis. Puerarin was administered to mastitis mice via intraperitoneal injection. The iron concentration was measured using an iron assay. TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the mammary gland tissues were assessed using the ELISA kits. The signaling pathways were detected by western blot analysis. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed that puerarin reversed pathological injury to mammary gland tissue induced by S. aureus. Puerarin also inhibited TNF-α and IL-1β production induced by S. aureus. The significant increases in iron concentration, myeloperoxidase activity, and the malondialdehyde (MDA) level in the mammary gland tissue were attenuated by puerarin. Moreover, puerarin treatment significantly reversed the decreases in the relative glutathione (GSH) and GPX4 expression. In addition, puerarin increased the expression of SIRT1 and solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) and decreased p53 expression. In vitro, the inhibitory effects of puerarin on S. aureus-induced inflammation and ferroptosis were prevented by the SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527. In conclusion, the therapeutic mechanism of puerarin involves the activation of the SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 pathway to inhibit ferroptosis and the inflammatory response.IMPORTANCEAntibiotics are the main drugs used to treat mastitis, but they can easily cause bacterial resistance and food safety issues. Therefore, finding safe and effective drugs is crucial to prevent and treat mastitis. Puerarin is the main isoflavonoid active ingredient in Pueraria lobata and has a wide range of pharmacological effects. We found that it could attenuate mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus.
Keywords: SIRT1; ferroptosis; inflammation; mastitis; puerarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Schisandrin B inhibits inflammation and ferroptosis in S.aureus-induced mastitis through regulating SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112430. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112430. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38852519
-
Gardenoside attenuates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis through Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):e0226224. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02262-24. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39612214 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of acupuncture on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway in rat models].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Aug 12;45(8):1099-1110. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20240703-k0003. Epub 2025 May 14. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40825694 Chinese.
-
Paclitaxel Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Macrophage Ferroptosis and Improving Lipid Metabolism via the Sirt1/Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway.FASEB J. 2025 Aug 15;39(15):e70917. doi: 10.1096/fj.202501047RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40779351
-
Utilization of probiotics against virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus in bovine mastitis.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Aug 7;118(9):125. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02138-0. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40775396 Review.
References
-
- Wang Y, Nan X, Zhao Y, Jiang L, Wang H, Zhang F, Hua D, Liu J, Yao J, Yang L, Luo Q, Xiong B. 2021. Dietary supplementation of inulin ameliorates subclinical mastitis via regulation of rumen microbial community and metabolites in dairy cows. Microbiol Spectr 9:e0010521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00105-21 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

