Development and evaluation of a 99mTc-labeled olaparib analog for PARP imaging
- PMID: 40694243
- PMCID: PMC12283529
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-025-00373-4
Development and evaluation of a 99mTc-labeled olaparib analog for PARP imaging
Abstract
Background: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is an important therapeutic target in cancer treatment, and dynamic assessment of its expression level is essential for achieving precision therapy. Although 18F-labeled PARP-targeted radiotracers have demonstrated remarkable tumor-imaging capabilities in preclinical studies, their high lipophilicity leads to increased non-specific uptake in abdominal organs, which has severely hindered their clinical translation. Furthermore, while PET imaging provides superior resolution and sensitivity, its infrastructure and operational demands may limit widespread accessibility in certain regions. Therefore, the development of SPECT-based PARP radiotracers could offer a complementary approach, potentially expanding access to PARP imaging in a broader range of clinical settings. To provide a more affordable and accessible alternative to PET probes, hydrazinonicotinamide (HYNIC)-olaparib was radiolabeled with technetium-99m (99mTc) and evaluated both in vitro and in vivo using the MDA-MB-453 breast cancer model.
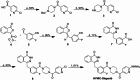
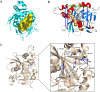
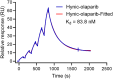
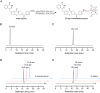
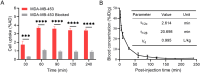
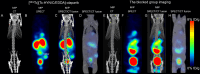
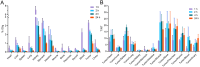
Results: [99mTc][Tc-HYNIC/EDDA]-olaparib exhibits a high radiochemical yield (> 90%), excellent radiochemical purity (> 90%), and good in vitro stability. The introduction of ethylenediamine-N, N'-diacetic acid (EDDA) and tricine facilitated the synthesis of 99mTc complex, and improved the hydrophilicity (logP = 0.63 ± 0.25) of the probe as well, resulting in reduced the accumulation of radiation in the abdomen. In vitro results indicated that [99mTc][Tc-HYNIC/EDDA]-olaparib could target PRAP-1 in MDA-MB-453 cells. In vivo experiments, micro SPECT/CT imaging provided clear visualization of MDA-MB-453 tumors with significant tumor-to-background distinction, and accumulation of [99mTc][Tc-HYNIC/EDDA]-olaparib was quantified at 3.45 ± 0.17%ID/g at 1 h post intravenous injection.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that [99mTc][Tc-HYNIC/EDDA]-olaparib holds great promise as a novel radiotracer for PARP imaging.
Keywords: 99mTc; Cancer diagnosis; Olaparib; PARP; SPECT imaging.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of Jiangsu Institute of Nuclear Medicine (Ethical Clearance Code: JSINM-2024-114). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cardoso F, Paluch-Shimon S, Senkus E, Curigliano G, Aapro MS, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya GS, Biganzoli L, Boyle F, Cardoso MJ, Carey LA, Cortés J, El Saghir NS, Elzayat M, Eniu A, Fallowfield L, Francis PA, Gelmon K, Gligorov J, Haidinger R, Harbeck N, Hu X, Kaufman B, Kaur R, Kiely BE, Kim SB, Lin NU, Mertz SA, Neciosup S, Offersen BV, Ohno S, Pagani O, Prat A, Penault-Llorca F, Rugo HS, Sledge GW, Thomssen C, Vorobiof DA, Wiseman T, Xu B, Norton L, Costa A, Winer EP. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1623–49. 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
