The role of LAMA5 in breast cancer progression and its potential in immunotherapy
- PMID: 40694271
- PMCID: PMC12283511
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03113-x
The role of LAMA5 in breast cancer progression and its potential in immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Laminin alpha-5 (LAMA5), a major extracellular matrix component, is involved in tumor progression by modulating cell adhesion, migration, and tissue architecture. However, its specific role in breast cancer (BRCA) remains unclear.
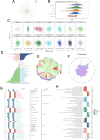
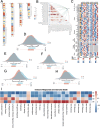
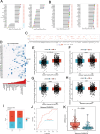
Methods: We analyzed LAMA5 expression in BRCA and normal tissues using TCGA and GTEx datasets. Differential expression analysis was conducted using DESeq2. Survival associations were assessed using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression models. GSEA was performed to identify LAMA5-related biological pathways. Immune infiltration was evaluated using CIBERSORT and ESTIMATE algorithms. Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics were used to explore the spatial distribution and cellular localization of LAMA5. Drug sensitivity and immunotherapy response analyses were also conducted.
Results: LAMA5 was significantly downregulated in BRCA tissues compared to normal tissues. Higher LAMA5 expression was associated with better recurrence-free and overall survival. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that LAMA5 is involved in immune regulation and extracellular matrix-related pathways. Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics demonstrated spatial and cellular heterogeneity of LAMA5 expression in BRCA. Immune-related analyses suggested that LAMA5 may influence immune cell infiltration and contribute to immune microenvironment remodeling. ROC analysis indicated moderate predictive value for immunotherapy response (AUC = 0.704), and LAMA5 expression was positively associated with sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents including cisplatin and docetaxel.
Conclusion: LAMA5 is a potential prognostic biomarker in BRCA and may play a dual role in modulating tumor progression and immune responses. Its association with drug sensitivity and immunotherapy outcomes highlights its value as a potential therapeutic target in precision oncology.
Keywords: Breast Cancer (BRCA); Immune modulation; LAMA5; Prognostic biomarker.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: This study utilized publicly available datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and other databases, which do not require ethical approval as per the guidelines established by the Declaration of Helsinki and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services regulations. Consent for publication: Consent for publication is not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sherman-Baust CA, Weeraratna AT, Rangel LB, Pizer ES, Cho KR, Schwartz DR, et al. Remodeling of the extracellular matrix through overexpression of collagen VI contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(4):377–86. - PubMed
-
- Tunggal P, Smyth N, Paulsson M, Ott MC. Laminins: structure and genetic regulation. Microsc Res Tech. 2000;51(3):214–27. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
