Evaluation of sequencing reads at scale using rdeval
- PMID: 40694478
- PMCID: PMC12401588
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf416
Evaluation of sequencing reads at scale using rdeval
Abstract
Motivation: Large sequencing datasets are being produced and deposited into public archives at unprecedented rates. The availability of tools that can reliably and efficiently generate and store sequencing read summary statistics has become critical.
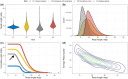
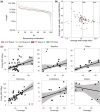
Results: As part of the effort by the Vertebrate Genomes Project (VGP) to generate high-quality reference genomes at scale, we sought to address the community's need for efficient sequence data evaluation by developing rdeval, a standalone tool to quickly compute and interactively display sequencing read metrics. Rdeval can either run on the fly or store key sequence data metrics in tiny read 'snapshot' files. Statistics can then be efficiently recalled from snapshots for additional processing. Rdeval can convert fa*[.gz] files to and from other popular formats including BAM and CRAM for better compression. Overall, while CRAM achieves the best compression, the gain compared to BAM is marginal, and BAM achieves the best compromise between data compression and access speed. Rdeval also generates a detailed visual report with multiple data analytics that can be exported in various formats. We showcase rdeval's functionalities using long-read data from different sequencing platforms and species, including human. For PacBio long-read sequencing, our analysis shows dramatic improvements in both read length and quality over time, as well as the benefit of increased coverage for genome assembly, though the magnitude varies by taxa.
Availability and implementation: Rdeval is implemented in C++ for data processing and in R for data visualization. Precompiled releases (Linux, MacOS, Windows) and commented source code for rdeval are available under MIT license at https://github.com/vgl-hub/rdeval. Documentation is available on ReadTheDocs (https://rdeval-documentation.readthedocs.io). Rdeval is also available in Bioconda and in Galaxy (https://usegalaxy.org). An automated test workflow ensures the consistency of software updates.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Update of
-
Evaluation of sequencing reads at scale using rdeval.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 8:2025.02.01.636073. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.01.636073. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2025 Sep 1;41(9):btaf416. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf416. PMID: 39975369 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Altmanová M, Rovatsos M, Kratochvíl L et al. Minute Y chromosomes and karyotype evolution in Madagascan iguanas (Squamata: Iguania: Opluridae). Biol J Linn Soc 2016;118:618–33.
-
- Andrews S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data [Online], 2010. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
-
- Baid G, Cook DE, Shafin K et al. DeepConsensus improves the accuracy of sequences with a gap-aware sequence transformer. Nat Biotechnol 2023;41:232–8. - PubMed
-
- Bankevich A, Bzikadze AV, Kolmogorov M et al. Multiplex de Bruijn graphs enable genome assembly from long, high-fidelity reads. Nat Biotechnol 2022;40:1075–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

