Identification and validation of oxidative stress-related genes for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 40694561
- PMCID: PMC12282930
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327945
Identification and validation of oxidative stress-related genes for the diagnosis of sepsis-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
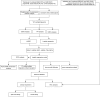
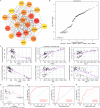
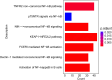
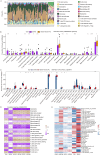
Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) is an inflammatory pulmonary condition characterized by a complex pathophysiological mechanism. The development and progression of sepsis-induced ALI are accompanied by significant oxidative damage. This study aimed to identify key oxidative stress-related genes associated with sepsis-induced ALI. Samples, including sepsis, sepsis-induced ALI, and control groups, were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Key oxidative stress-related genes in sepsis-induced ALI were identified using Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA), Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network analysis, logistic regression, and LASSO regression analysis. Functional information regarding these genes was explored through Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). A logistic regression model was constructed based on the identified hub oxidative stress-related genes. The diagnostic value of this model for sepsis-induced ALI was assessed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The relative abundance of 22 human immune cell types was calculated using CIBERSORT software. The expression levels of hub genes in the blood samples of sepsis-induced ALI patients were analyzed through RT-PCR and ELISA. A total of 1,055 genes associated with sepsis-induced ALI were identified via WGCNA, of which 145 genes were linked to oxidative stress. GSVA revealed that these 145 genes were significantly enriched in 79 biological pathways, while GSEA indicated a strong association with immune-related signaling pathways. Additionally, the top 20 genes were selected through PPI network analysis. The logistic regression model was constructed using VDAC1, HSPA8, SOD1, HSPA9, TXN, and SNCA. In the training set and the validation set, the AUC values of logistic regression model were 0.9091 and 0.8279, respectively, suggesting good discriminability when distinguishing normal from sepsis-induced ALI. Notably, these six genes were correlated with immune cell infiltration in sepsis-induced ALI, with HSPA8, SOD1, and HSPA9 showing downregulation in sepsis-induced ALI. In conclusion, VDAC1, HSPA8, SOD1, HSPA9, TXN, and SNCA have been identified as oxidative stress-related genes associated with sepsis-induced ALI. The logistic regression model developed using these six genes could identify patients with sepsis-induced ALI. Our findings might provide novel research strategies for the molecular therapeutic target of sepsis-induced ALI.
Copyright: © 2025 Fu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and verification of immune and oxidative stress-related diagnostic indicators for malignant lung nodules through WGCNA and machine learning.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04639-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594252 Free PMC article.
-
The role of senescence-related hub genes correlating with immune infiltration in type A aortic dissection: Novel insights based on bioinformatic analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0326939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326939. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40561071 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning based screening of biomarkers associated with cell death and immunosuppression of multiple life stages sepsis populations.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14600-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830558 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

