Identification of SnRNA U6 as an endogenous reference gene for normalization of MiRNA expression data in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 40695852
- PMCID: PMC12284167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04062-9
Identification of SnRNA U6 as an endogenous reference gene for normalization of MiRNA expression data in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
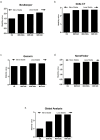
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, exhibits structural differences compared to other coronaviruses that impact transmission dynamics and host response. Although vaccines have reduced severe hospitalizations and deaths, understanding the infection remains challenging, and finding viable biomarkers for disease severity would be beneficial. In this context, microRNAs (miRNAs) are a set of small non-coding RNAs that have emerged as potential biomarkers for numerous diseases. However, assessing miRNA expression requires the normalization of RT-qPCR data using appropriate endogenous reference genes. The selection of these reference genes remains a major challenge, directly impacting the accuracy of expression analyses. Although several small RNAs, including snRNAs, have been evaluated, there is still no consensus regarding the optimal reference genes for the normalization of plasma miRNA expression data in COVID-19 infection. This study evaluated five candidate genes-including RNU6B, snRNA U6 (small nuclear RNAs) and three miRNAs (miR-320a, miR-342-3p, and miR-328) as potential endogenous normalizers for analyzing miRNA expression in the plasma of COVID-19 patients. The snRNA U6 showed greater stability using a combination of statistical algorithms (NormFinder, RefFinder, BestKeeper, and GeNorm), indicating that this snRNA can be used as a robust internal reference for analysis in the plasma of COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Covid-19; Normalization; RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2; miRNA; snRNAU6.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
microRNAs for qPCR Normalization Under Morphofunctional Conditions in Bovine Sperm (Bos taurus).Mol Reprod Dev. 2025 Aug;92(8):e70045. doi: 10.1002/mrd.70045. Mol Reprod Dev. 2025. PMID: 40767510 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary collaborative guidance on the assessment and treatment of patients with Long COVID: A compendium statement.PM R. 2025 Jun;17(6):684-708. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.13397. Epub 2025 Apr 22. PM R. 2025. PMID: 40261198
References
-
- Cevik, M., Kuppalli, K., Kindrachuk, J. & Peiris, M. Virology, transmission, and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2. BMJ371, 1–6 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Eastin, C. & Eastin, T. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. J. Emerg. Med.58, 711–712 (2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 88887.644892/2021-00/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- 0494/20-01.20.0026.00/Programa Laboratórios de Campanha do Ministério de Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação - MCTI/FINEP
- Outorga nº SUS0032/2021/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia - FAPESB, Edital 02/2020 - Programa Pesquisa para o SUS: gestão compartilhada em saúde - PPSUS
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

