Amino acid-based deep eutectic solvent as a versatile catalyst for the green synthesis of chromenopyrimidines
- PMID: 40695859
- PMCID: PMC12283943
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08820-7
Amino acid-based deep eutectic solvent as a versatile catalyst for the green synthesis of chromenopyrimidines
Abstract
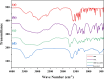
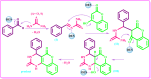
A novel deep eutectic solvent (Thr/Mal-DES) was synthesized by mixing one mole of L-threonine (Thr) with one mole of malonic acid (Mal) and was characterized by FT-IR, 1H NMR, TGA/DTA, and densitometry techniques. Then, it was used as a highly effective catalyst for the rapid synthesis of chromeno[4,3-d]pyrimidines from the reaction of 4-hydroxy-coumarin, urea/thiourea and aldehyde under solvent-free conditions at 80 °C in high yields and short reaction times.
Keywords: Catalysis; Chromenopyrimidines; Deep eutectic solvent; L-threonine; Malonic acid.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

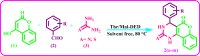





References
-
- Hayyan, M. et al. Saheed, O. K. Are deep eutectic solvents benign or toxic. Chemosphere90, 2193–2195 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Dai, Y., Van Spronsen, J., Witkamp, G. J., Verpoorte, R. & Choi, Y. H. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents in natural products research: Mixtures of solids as extraction solvents. J. Nat. Prod.76, 2162–2173 (2013). - PubMed
-
- de Domínguez, P. Recent trends in (ligno) cellulose dissolution using neoteric solvents: Switchable, distillable and bio-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol.89, 11–18 (2014).
-
- Buzatu, A. R., Todea, A., Peter, F. & Boeriu, C. G. The role of reactive natural deep eutectic solvents in sustainable biocatalysis. ChemCatChem13, e202301597 (2024).
-
- Santana-Mayor, Á., Rodríguez-Ramos, R., Herrera-Herrera, A. V., Socas-Rodríguez, B. & Rodríguez-Delgado, M. Á. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem.134, 116108 (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

