Exploration of plasma exosomal miR-122-5p and its related targets KNG1 and C3 in the diagnosis of drug-resistant tuberculosis
- PMID: 40695929
- PMCID: PMC12284156
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10639-1
Exploration of plasma exosomal miR-122-5p and its related targets KNG1 and C3 in the diagnosis of drug-resistant tuberculosis
Abstract
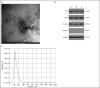
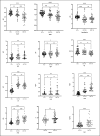
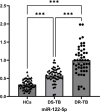
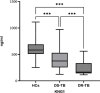
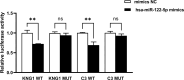
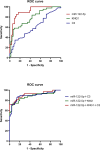
Drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) poses significant challenges not only to public health but also imposes substantial psychological and economic burdens on individuals and their families. As a severe infectious disease that jeopardizes both physical and mental well-being, DR-TB frequently spreads in underdeveloped regions due to inadequate diagnostic technologies.In this study, we validated the binding interaction between miR-122-5p and the proteins kininogen-1 (KNG1)/complement C3 using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Furthermore, we employed liquid biopsy techniques to quantify miR-122-5p expression in plasma exosomes from DR-TB patients, alongside measuring plasma levels of KNG1, complement C3, and other coagulation and immune function parameters. This approach aims to identify efficient, non-invasive laboratory biomarkers for the early diagnosis of DR-TB. 50 patients with drug-susceptible tuberculosis (DS-TB) and 50 patients with DR-TB who were diagnosed in the nearby hospital between April 2024 and January 2025 were chosen. 51 healthy people who had physical exams over the same time frame were also selected as the control group. In the early morning, 5 ml of fasting venous blood was drawn from each of all subjects and centrifuged for standby. Informed consent was obtained from all Participants, who then signed the informed consent forms. We used Western blotting (WB), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) to find the biomarkers in the exosomes that were taken from each of the three groups' plasma. The dual-luciferase experiment was used to verify the targeting relationship between miR-122-5p and protein KNG1 and complement C3. The RNA level of the miR-122-5p gene in plasma exosomes was detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). The KNG1 level in the plasma of the subjects was measured by ELISA, and the clinical indicators of the patients were also collected. To assess the diagnostic effectiveness of the genes found in the plasma exosomes, we used the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. We found that there is a targeting relationship between miR-122-5p and protein KNG1 as well as complement C3. Meanwhile, the level of miR-122-5p in the DR-TB group was significantly higher than that in the DS-TB group and the HCs group, indicating a relatively high diagnostic efficacy. A useful biomarker to enhance the diagnosis of DR-TB is the level of miR-122-5p in plasma exosomes.
Keywords: Biomarker; Diagnosis; Exosome; Tuberculosis; miR-122-5p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, and the ethics number was 2024(E2)-KS-069. Consent for publication: Yes.
Figures
References
-
- Fogel, N. Tuberculosis: a disease without boundaries. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 95, 527–531 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Jumat, M. I., Sarmiento, M. E., Acosta, A. & Chin, K. L. Role of non-coding RNAs in tuberculosis and their potential for clinical applications. J. Appl. Microbiol.134, lxad104 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Behrooz, M., Hajjarzadeh, S., Kahroba, H., Ostadrahimi, A. & Bastami, M. Expression pattern of miR-193a, miR122, miR155, miR-15a, and miR146a in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children with obesity and their relation to some metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers. BMC Pediatr.23, 95 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

