Multifactorial analysis of radiochemical purity in high-activity 177Lu-labeled theranostics: impact of precursor source, 177Lu form, and production parameters
- PMID: 40696084
- PMCID: PMC12283506
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-025-00372-5
Multifactorial analysis of radiochemical purity in high-activity 177Lu-labeled theranostics: impact of precursor source, 177Lu form, and production parameters
Abstract
Background: Lutetium-177 (177Lu) theranostics have revolutionized personalized cancer treatment, particularly with FDA-approved therapies like [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE for neuroendocrine tumors and [177Lu]Lu-PSMA for prostate cancer. Despite growing clinical adoption, there is limited understanding of how different production variables affect radiochemical purity, especially when scaling to high activities for multi-patient batches. This study evaluates the impact of precursor sources, 177Lu forms (carrier-added (C.A) vs. non- carrier-added (N.C.A)), and radiochemical concentration on product quality.
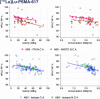
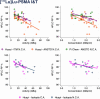
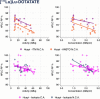
Results: We analyzed 355 clinical batches of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE (n = 101), [177Lu]Lu- PSMA-617 (n = 169), and [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T (n = 85) produced with standardized protocols using lutetium-177 from multiple suppliers in both carrier-added and non-carrier-added forms. All radiopharmaceuticals demonstrated consistently high yields (≥ 98%) and met release criteria regardless of starting materials. [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE and [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 maintained radiochemical purity above 90% throughout 24 h, while [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T showed stability for 8 h but fell below specifications at 24 h. Negative correlations between bulk activity/concentration and radiochemical purity were observed across all preparations. The lutetium-177 products from various suppliers displayed notably distinct quality profiles. Some suppliers consistently provided higher radiochemical purities, irrespective of the carrier-added or non-carrier-added forms of lutetium-177. However, carrier- added formulations exhibited greater radiostability compared to non-carrier-added ones at elevated concentrations. Furthermore, differences in precursor quality among manufacturers were noted, with certain suppliers offering enhanced radiostability characteristics that may enhance product performance at high activity concentrations.
Conclusion: This comprehensive analysis reveals that hospital-based production can be automized resulting in high-quality and efficient multi-dose production. Small differences in radiochemical purity of 177Lu -labeled theranostics depends on complex interactions between precursor source, 177Lu supplier, and 177Lu form, beyond simple activity-dependent radiolysis. These findings underscore the importance of optimizing production parameters for high- activity preparations and highlight the need to explore the various multifactorial variables that impact the quality of 177Lu-theranostics.
Keywords: Carrier-added lutetium-177; DOTATATE; High-activity production; Lutetium-177 theranostics; Non-carrier-added lutetium-177; PSMA-617; PSMA-I&T; Quality control; Radiochemical purity; Radiolysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel-Wahab M, Giammarile F, Carrara M, Paez D, Hricak H, Ayati N, et al. Radiotherapy and theranostics: a Lancet oncology commission. Lancet Oncol. 2024;25(11):e545–80. - PubMed
-
- Azad AA, Bressel M, Tan H, Voskoboynik M, Suder A, Weickhardt AJ, et al. Sequential [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and docetaxel versus docetaxel in patients with metastatic hormone- sensitive prostate cancer (UpFrontPSMA): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2024;25(10):1267–76. - PubMed
-
- Boasa CV, Diasa L, Matsudaa M, Araújoa E. Stability in the production and transport of 177Lu labelled PSMA. Braz J Radiat Sci. 2021. 10.15392/bjrs.v9i1.1619. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
