Burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in milk among middle-aged and elderly population from 1990 to 2021: a population-based study
- PMID: 40696191
- PMCID: PMC12283431
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-025-03129-x
Burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in milk among middle-aged and elderly population from 1990 to 2021: a population-based study
Abstract
Objective: This study examines the global burden of colorectal cancer (CRC) attributable to diet low in milk among middle-aged and elderly populations from 1990 to 2021 and projects future trends to 2050.
Methods: Data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study were obtained via the Global Health Data Exchange. The burden was assessed using number of cases and rates of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALY) and death, stratified by age, sex, region, nation, and Socio-Demographic Index (SDI). Temporal trends were analyzed using estimated annual percentage change (EAPC), and future trends were projected using the Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) model.
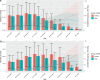
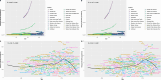
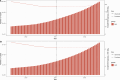
Results: In 2021, the global DALY and death cases of CRC attributable to a diet low in milk among middle-aged and elderly populations was 2.71 million and 0.14 million, respectively, representing increases of 92.81% and 103.02% from 1990. However, the corresponding DALY and death rates decreased from 209.65 to 182.64 per 100,000 population and from 9.96 to 9.13 per 100,000 population, respectively, with EAPCs of - 0.54 and - 0.36. The DALY and death rates rise with age, peaking in the 95 + age group. From 1990 to 2021, among regions, Southern Sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Europe saw the largest increases in these rates, while Australasia, High-income North America, and Western Europe had the largest decreases. At the national level, Lesotho, Cabo Verde, and Georgia saw the largest increases in the DALY and death rates, while Austria, Australia, and Germany experienced the largest decreases. The correlation analysis showed that the DALY and death rates across 21 regions increased with rising SDI levels up to approximately 0.67, then declined and stabilized. Projections suggest a significant rise in DALY and death cases, with a slight increase in DALY and death rates.
Conclusions: The burden of CRC attributable to a diet low in milk remains substantial among middle-aged and elderly populations globally, with significant age, sex, regional and national disparities. These findings highlight the need for targeted dietary interventions to mitigate the growing burden of CRC among middle-aged and elderly populations.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Diet low in milk; Global Burden of Disease; Middle-aged and elderly population; Public health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Human and animal rights: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Washington. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent: For this type of study, formal informed consent is not required.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global burden of cardiovascular disease due to low physical activity, 1990-2021.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11329-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40665118 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of Breast Cancer Attributable to a Diet High in Red Meat at Global, Regional, and National Levels: An Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Arch Iran Med. 2025 May 1;28(5):275-285. doi: 10.34172/aim.34079. Epub 2025 May 1. Arch Iran Med. 2025. PMID: 40751521 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic stroke in the context of high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: A 30-year global burden perspective of 204 nations.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2025 Aug 6;34(10):108418. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2025.108418. Online ahead of print. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40780550
-
Global burden and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders among adolescents and young adults in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019.Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Aug;22(8):103361. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103361. Epub 2023 May 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2023. PMID: 37230312 Review.
-
National and subnational burden of brain and central nervous system cancers in China and global from 1990 to 2021: results from the global burden of disease study 2021.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jul 28;83(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13690-025-01683-4. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40722045 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

