Artificial intelligence in predicting macular hole surgery outcomes: a focus on optical coherence tomography parameters
- PMID: 40696275
- PMCID: PMC12281962
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04256-9
Artificial intelligence in predicting macular hole surgery outcomes: a focus on optical coherence tomography parameters
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the predictive performance of optical coherence tomography (OCT)-based indices and artificial intelligence (AI) using a Generative Pre-Trained Transformer (GPT) model and compare them with traditional logistic regression in forecasting anatomical success following macular hole (MH) surgery.
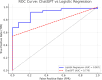
Methods: This retrospective observational study included 51 eyes of 51 patients who underwent pars plana vitrectomy for idiopathic MH. Preoperative OCT measurements of macular hole index (MHI), traction hole index (THI), hole form factor (HFF), basal hole diameter (BHD), and minimum hole diameter (MHD) were recorded. GPT-based AI predictions were generated using masked input data. A logistic regression model was developed with the same variables. Predictive performance was assessed using accuracy, area under the curve (AUC), positive predictive value (POPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and Kappa statistics.
Results: Anatomical success was achieved in 72.5% of cases. MHI, THI, and HFF were significantly higher in the successful group (p < 0.0001). GPT achieved an accuracy of 77.0% and AUC of 0.770, with perfect POPV (1.000) but low NPV (0.452). Logistic regression outperformed GPT, achieving an accuracy of 84.3%, an AUC of 0.759, a higher NPV (0.800), and better agreement (Kappa 0.568 vs. 0.392). BHD and MHD showed poor predictive power (AUC 0.291).
Conclusion: OCT-derived indices, especially MHI, THI, and HFF, effectively predict MH surgery outcomes. Logistic regression based on actual patient data demonstrated superior predictive performance compared to GPT. AI models hold potential but require further development, integration of multimodal data, and validation before clinical application.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; BHD; GPT; HFF; MHI; Macular hole; THI.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Kartal Dr. Lutfi Kirdar City Hospital Clinical Research Ethics Committee, a body that upholds the highest ethical standards in medical research, approved the study, providing reassurance about the ethical conduct of our research. (2025/010.99/13/26) This research complied with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The requirement for obtaining written informed consent from participants was waived by the Lutfi Kirdar City Hospital Clinical Research Ethics Committee due to the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
External limiting membrane aperture as a reliable and predictive prognostic factor in macular hole surgery.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025 Sep;35(5):1854-1862. doi: 10.1177/11206721251334161. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40232276
-
Anatomical and Functional Outcome Following Surgery of Idiopathic Macular Hole.Mymensingh Med J. 2025 Jul;34(3):881-886. Mymensingh Med J. 2025. PMID: 40583682
-
Vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling versus vitrectomy with no peeling for idiopathic full-thickness macular hole (FTMH).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 5;(6):CD009306. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009306.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23740611
-
Vitrectomy for idiopathic macular hole.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 12;2015(5):CD009080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009080.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25965055 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
References
-
- Yang LWY, Ng WY, Foo LL, Liu Y, Yan M, Lei X, et al. Deep learning-based natural language processing in ophthalmology: applications, challenges and future directions. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2021;32(5):397–405. 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000789. - PubMed
-
- OpenAI. GPT-4 Technical Report. 2023. Available from: https://openai.com/research/gpt-4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

