Botulinum toxin type A inhibits microglia pyroptosis by suppressing Cblb-mediated degradation of Pdlim1 to attenuate neuropathic pain
- PMID: 40696327
- PMCID: PMC12281680
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-025-02109-w
Botulinum toxin type A inhibits microglia pyroptosis by suppressing Cblb-mediated degradation of Pdlim1 to attenuate neuropathic pain
Abstract
Background: Microglia pyroptosis, a newly identified form of inflammatory cell death, is involved in the development of neuropathic pain (NP). Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) has been shown to be effective in relieving NP, but the mechanisms involved have not been clarified.
Methods: A mice model of NP was established with chronic constriction injury (CCI) method. The expression levels of key molecules and the extent of microglia pyroptosis were assessed using RT-qPCR, western blot, ELISA and immunofluorescence. Moreover, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used in vitro to induce pyroptosis of microglia to explore the potential molecular mechanisms of BTX-A.
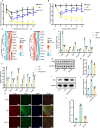
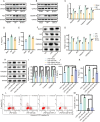
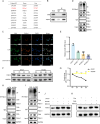
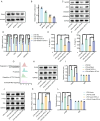
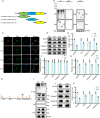
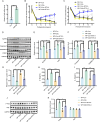
Result: In a mice model of NP, BTX-A administration increased the pain threshold and decreased the Cblb protein expression level, consistent with the results of in vitro experiments. Functional experiments and mouse models were respectively used to evaluate the severity of microglia pyroptosis. The results showed that BTX-A inhibited microglia pyroptosis through Cblb protein. Subsequently, mass spectrometry (MS) analysis and immunoprecipitation were conducted to identify proteins interacting with Cblb. The results identified Pdlim1 was a potential interacting partner of Cblb, which regulats the ubiquitination of Pdlim1. Mechanically, Cblb binds to the PDZ and LIM domains of Pdlim1 and then targets Pdlim1 at K244 for ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. Pdlim1 knockdown lentiviral plasmid was constructed and stable Pdlim1 knockdown microglial cell lines were established for rescue experiments. The results demonstrated that BTX-A suppresses microglia pyroptosis via Pdlim1/NF-κB signaling axis. Finally, intrathecal injection of adeno-associated virus overexpressing Cblb was used in rescue experiments. The results confirmed that BTX-A attenuates neuropathic pain via the Cblb/Pdlim1/NF-kB signaling axis.
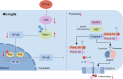
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that BTX-A suppresses the activity of Cblb, thereby reducing Pdlim1 protein degradation, inhibiting the NF-kB pathway, and ultimately mitigating microglia pyroptosis. Our findings suggest that Cblb could serve as a novel therapeutic target for BTX-A in the treatment of NP.
Keywords: BTX-A; Cblb; Microglia pyroptosis; Neuropathic pain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: We have complied with all relevant ethical regulations for animal testing and research. The experimental design was approved by the Ethics Committee of Laboratory Animal Welfare of Nanchang University. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGR2 maintains neuropathic pain by promoting microglial phagocytosis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Apr 28;50(4):586-601. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240270. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40785673 Free PMC article.
-
NaHS alleviates neuropathic pain in mice by inhibiting IL-17-mediated dopamine (DA) neuron necroptosis in the VTA.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Jan;220:111168. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111168. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39672209
-
TREM-1 as a potential gatekeeper of neuroinflammatory responses: therapeutic validation and mechanistic insights in experimental traumatic brain injury.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1636917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1636917. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40761800 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management of functional bladder outlet obstruction in adults with neurogenic bladder dysfunction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 24;2014(5):CD004927. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004927.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24859260 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 27;2014(4):CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 09;6:CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub4. PMID: 24771480 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024YNFY12028/National Natural Science Foundation incubation program of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University
- 2023YNFY12019/National Natural Science Foundation incubation program of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University
- 82160227/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20224BAB206036/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province
- GJJ210125/Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education Science and Technology Program Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

