The mediating effects of psychological capital and career success in the relationship between leadership styles and job satisfaction among nurse managers: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40696330
- PMCID: PMC12281739
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-025-03616-6
The mediating effects of psychological capital and career success in the relationship between leadership styles and job satisfaction among nurse managers: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
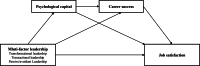
Background: Nursing managers' leadership styles significantly influence their job satisfaction, yet the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study explores the mediating roles of psychological capital and career success in the relationship between leadership styles-transformational (TFL), transactional (TSL), and passive/avoidant (PAL)-and job satisfaction (JS).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in May 2024 with nurse managers from 20 hospitals in Henan Province, China. Of 810 contacted, 784 participated. Participants completed validated instruments, including the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire, Psychological Capital Scale, Career Success Scale, and Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. Pearson's correlation and serial mediation analyses were performed using IBM SPSS (version 21) and the PROCESS macro (version 3.4).
Results: Both TFL and TSL had direct and positive effects on JS, with psychological capital and career success serving as partial mediators. Significant sequential mediation effects were found for both styles-for example, TFL→ psychological capital → career success →JS (β = 0.112, 95% CI [0.073, 0.155]) and TSL→ psychological capital → career success →JS (β = 0.260, 95% CI [0.188, 0.339]). In contrast, PAL showed no significant direct or total indirect effect on JS, though the sequential mediation pathway via psychological capital and career success was significant (β =-0.077, 95% CI [-0.122, -0.035]).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that both TFL and TSL significantly influence nurse managers' job satisfaction, not only through direct effects but also indirectly via psychological capital and career success, including their sequential mediation. These findings highlight the critical role of leadership in enhancing psychological resources and career development. Strengthening effective leadership styles may serve as a strategic pathway to fostering a more supportive work environment and improving job satisfaction in healthcare settings.
Keywords: Career success; Job satisfaction; Leadership style; Nurse manager; Psychological capital; Serial mediation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The research received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of Henan Provincial People’s Hospital (Ethics Approval No. (2024) Lun Shen No. 114). The research was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided informed consent prior to participation. Anonymity was ensured through the online survey, and consent was obtained when individuals accessed the survey link Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Marquis BL, Huston CJ. Leadership Roles and Management Functions in Nursing: theory and Application. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009.
-
- Thorpe K, Loo R. Balancing professional and personal satisfaction of nurse managers: current and future perspectives in a changing health care system. J Nurs Manag. 2003;11(5):321–30. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Aungsuroch Y, Yunibhand J. Job satisfaction in nursing: a concept analysis study. Int Nurs Rev. 2016;63(1):84–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources