Identification of novel biomarkers involved in oral squamous cell carcinoma by whole transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 40696350
- PMCID: PMC12285194
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03913-9
Identification of novel biomarkers involved in oral squamous cell carcinoma by whole transcriptome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is among the most common malignant tumors in the oral and maxillofacial regions, characterized by high drug resistance and poor treatment outcomes. This underscores the urgent need to identify novel biomarkers for OSCC.
Methods: Differentially expressed messenger RNAs (mRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (DE-mRNAs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-lncRNAs) between primary and control groups, as well as metastatic and primary groups, were identified using whole transcriptome sequencing data. Candidate OSCC genes were derived from DE-mRNAs. Potential biomarkers were then identified using five algorithms from CytoHubba. Biomarkers were validated via univariate Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier (K-M) survival analysis. Additional analyses included subcellular localization, mutation analysis, and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). Key drugs for OSCC treatment were also identified. Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry were employed to verify the expression levels of key biomarkers.
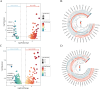
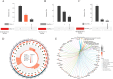
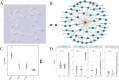
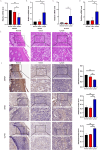
Results: A total of 304 candidate genes were identified, with 29 potential biomarkers selected by five algorithms. ANPEP, APOB, GLP1R, and SI exhibited significant survival differences in the K-M curves, establishing them as OSCC biomarkers. These biomarkers were predominantly localized in the cytoplasm, with SI and APOB showing the highest mutation susceptibility. Enrichment analysis revealed that the 'interferon-gamma response'biological function was co-enriched by ANPEP, APOB, and SI. Furthermore, BIBW2992 (afatinib) and PF.02341066 (crizotinib) were most strongly correlated with the biomarkers, suggesting their potential as key drugs for OSCC treatment. Additionally, the findings were validated by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemical analyses, and the results were consistent with the RNA-seq data.
Conclusion: ANPEP, APOB, GLP1R, and SI were identified as potential OSCC biomarkers, offering valuable insights for further research and therapeutic development.
Keywords: Complete RNA sequencing; Drugs; Molecular indicators; Oral squamous carcinoma; Regulatory networks.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Lanzhou University (Ethics approval number: LDYYLL2024-776). The patients provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Consent for publication: This article has been authorized by all authors and agreed to be published. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

