Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction exerts gouty arthritis therapy by skewing macrophage polarization through butanoate metabolism
- PMID: 40696369
- PMCID: PMC12281712
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01162-6
Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction exerts gouty arthritis therapy by skewing macrophage polarization through butanoate metabolism
Abstract
Background: Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction (QZTBD), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of gouty arthritis. However, to date, the precise pharmacological mechanisms remain unclear.
Purpose: The study aims to ascertain the therapeutic effects and the underlying mechanisms of QZTBD in the treatment of gouty arthritis.
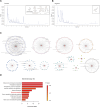
Methods: The efficacy and safety of different doses of QZTBD were investigated in Uox-KO mice. Candidate active ingredients were identified using UHPLC-MS/MS. The potential therapeutic pathways of the active ingredients were predicted through network pharmacology. The mechanisms of QZTBD in alleviating gouty arthritis were explored via comprehensive analyses of gut microbiota, combined with RT-qPCR, western blot, immunofluorescence, ELISA, flow cytometry, and Seahorse assay. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), bacterial culture experiment, butyrate-producing bacteria (BPB) and butyrate administration, and 2-DG intervention were conducted to explore the roles of BPB and butanoate metabolism in gout progression and therapeutic mechanisms of QZTBD. In vitro studies further validated the regulatory effects of butyrate and QZTBD on macrophage polarization through glycolysis modulation.
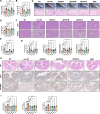
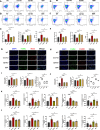
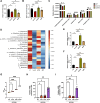
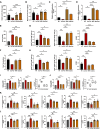
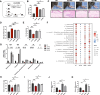
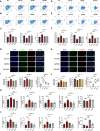
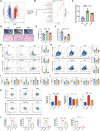
Results: 18.0 g/kg/d of QZTBD effectively alleviated the symptoms of gouty arthritis with excellent hepatic and renal safety. UHPLC-MS/MS analysis and network pharmacology revealed that QZTBD exerts its effects on butanoate metabolism during gouty arthritis inflammation. QZTBD treatment increased the abundance of BPB, the levels of serum and colon butyrate, and the expression levels of Buk and But. The transplantation of QZTBD-treated microbiota reproduced the therapeutic effects of QZTBD. M1 macrophage polarization was suppressed after QZTBD intervention. The administration of BPB and butyrate attenuated gouty arthritis and orchestrated macrophage polarization. Inhibition of glycolysis regulated the phenotype of macrophage and attenuated inflammatory processes. In vitro analysis unveiled that QZTBD and butyrate modulated glycolysis to regulate macrophage polarization, thereby alleviating gouty arthritis.
Conclusion: QZTBD targeted butanoate metabolism to regulate macrophage polarization, thereby effectively alleviating intestinal inflammation and restoring immune homeostasis in gouty arthritis. These findings establish a mechanistic foundation for developing precision therapeutic strategies leveraging QZTBD to combat gouty arthritis.
Keywords: Butanoate metabolism; Glycolysis; Gouty arthritis; Gut microbiome; Macrophage polarization; Qu-zhuo-tong-bi decoction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Approval No. IACUC-20210621-17; June 2021). All procedures were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and institutional ethical standards. Consent for publication: The authors declare no competing interests in relation to this study. All authors have read and consented to the published version of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declared there are no conflicts of interest for this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Qu-Zhuo-Tong-Bi Decoction Alleviates Gouty Arthritis by Regulating Butyrate-Producing Bacteria in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 2;11:610556. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.610556. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33603667 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated network pharmacology and gut microbiome analysis to reveal the mechanism of Qu-Zhuo-Tong-Bi decoction against hyperuricemia and gout.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;316:116736. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116736. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37286117
-
Wendan Decoction exerts therapeutic effects on insomnia by regulating gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolism.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157028. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157028. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40618491
-
Oral traditional Chinese medication for adhesive small bowel obstruction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;2012(5):CD008836. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008836.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22592734 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of recurrent Clostridioides difficile (Clostridium difficile).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Apr 25;4(4):CD013871. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013871.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37096495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J, Wu M, Yang J, Zhao D, He D, Liu Y, et al. Multimodal smart systems reprogramme macrophages and remove urate to treat gouty arthritis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024;19(10):1544–57. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

