Primary and secondary metastatic dissemination: multiple routes to cancer-related death
- PMID: 40696378
- PMCID: PMC12281838
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02389-5
Primary and secondary metastatic dissemination: multiple routes to cancer-related death
Abstract
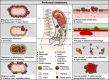
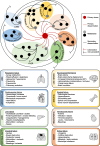
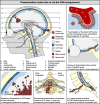
Metastatic disease accounts for approximately 80% of cancer-related deaths, typically manifesting as single-organ failure mainly through abdominal, cardiovascular, neurological, or respiratory complications. Despite treating thousands of cancer patients daily worldwide, our understanding of organ-specific metastatic dissemination routes, tissue destruction mechanisms and reasons for organ failures remains limited. As cancer-directed therapies advance, maintaining organ function has emerged as a critical therapeutic goal of care. To develop more effective treatment strategies, a comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiology is essential, particularly regarding secondary and subsequent metastatic waves that lead to extensive macro-metastases and organ failure. Critical distinction between primary metastatic spread and secondary intra-organ dissemination is crucial. In the era of precision oncology, elucidating organ-specific destruction processes and the pathophysiology of metastatic waves is fundamental for advancing patient care. To highlight the emerging goal of care of maintaining organ function, we aligned the metastatic biology, clinical stages, goals of care and therapeutic indications: the Bio Therapeutic Goals of Cancer Care Model.
Keywords: Bio Therapeutic Goals of Cancer Care Model; CNS; Cancer-directed therapy; Metastasis; Metastatic dissemination; Primary dissemination; Secondary dissemination.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Amberg JR. Dynamic Radiology of the Abdomen - Normal and Pathologic Anatomy - 2nd Edition - Meyers,Ma. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 1983;249(19):2695.
-
- Meyers MA. Distribution of intra-abdominal malignant seeding: dependency on dynamics of flow of ascitic fluid. Am J Roentgenol. 1973;119(1):2–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

