Hepatic stellate cell-specific miR-214 expression alleviates liver fibrosis without boosting steatosis and inflammation
- PMID: 40696410
- PMCID: PMC12285054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06880-x
Hepatic stellate cell-specific miR-214 expression alleviates liver fibrosis without boosting steatosis and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Liver fibrosis is a progressive pathological process primarily driven by the transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) into myofibroblast-like cells which secrete excessive extracellular matrix (ECM). Although microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as key regulators of fibrogenesis, the therapeutic potential and mechanistic specificity of miR-214-3p (miR-214) in liver fibrosis remain insufficiently defined.
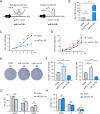
Methods: An adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based system was used to achieve either whole-liver or HSC-specific overexpression of miR-214 (via GFAP promoter) in a mouse model of alcohol-associated liver fibrosis induced by Lieber-DeCarli ethanol diet combined with low-dose CCl₄ injection. Liver fibrosis, steatosis, and inflammation were evaluated by biochemical assays, histology, immunostaining, and gene expression analyses. In vitro, stable miR-214 overexpression and knockdown in LX-2 cells were performed to assess effects on HSC proliferation, transdifferentiation, and ECM gene expression. MECP2 was identified as a direct functional target of miR-214 by bioinformatics and luciferase reporter assays.
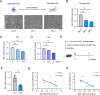
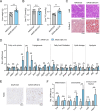
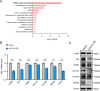
Results: miR-214 expression was significantly downregulated during HSC activation in vitro and in fibrotic livers. Whole-liver overexpression of miR-214 alleviated liver fibrosis but caused undesirable steatosis and inflammation. Notably, HSC-specific miR-214 overexpression ameliorated liver fibrosis without inducing these adverse effects. Functionally, miR-214 inhibited HSC proliferation and ECM gene expression, while its inhibition promoted this process. Mechanistically, miR-214 exerts its anti-fibrosis function at least in part by directing targeting MECP2, a critical regulator for HSC activation.
Conclusions: These findings not only identify miR-214 as a promising antifibrotic agent, but also highlight the translational advantage of cell-specific miRNA delivery. HSC-targeted miR-214 gene therapy may offer a promising and safer approach for treating liver fibrosis.
Keywords: AAV; Gene therapy; Hepatic stellate cell; Liver fibrosis; MiR-214.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Qingdao University (No. 20230901C577220240121151). All experimental procedures followed the approved guidelines. Consent for publication: All authors consent this manuscript for publication. Competing interests: The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures




References
-
- Senoo H. Structure and function of hepatic stellate cells. Med Electron Microsc. 2004;37:3–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

