Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with negative endoscopic biopsy and no peripheral eosinophilia: A case report
- PMID: 40696579
- PMCID: PMC12282817
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043289
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with negative endoscopic biopsy and no peripheral eosinophilia: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EoGE) is a rare inflammatory disease that can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract. Klein et al classified EoGE into 3 distinct subtypes according to the depth of eosinophilic infiltration: mucosal, muscular, and serosal.
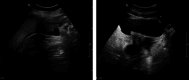
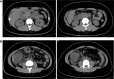
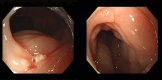
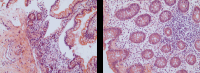
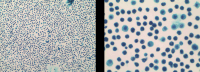
Patient concerns: We herein report a case of a 29-year-old woman who presented with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, with no history of adverse reactions to any allergens. Laboratory test results revealed a normal count of peripheral blood eosinophils. Ultrasound and computed tomography revealed thickened intestinal walls and ascites in both the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. Multiple endoscopic biopsies targeting several swelling segments of the intestinal wall revealed no increase in the number of eosinophils.
Diagnoses: The constellation of clinical, laboratory, radiological findings, histopathological data, and the excellent response to corticosteroids led to a diagnosis of EoGE for the patient.
Interventions: The patient was treated with corticosteroids.
Outcomes: Symptoms improved rapidly, and the thickened intestinal walls returned to a typical level.
Lessons: EoGE should be considered scrupulously, even if the count of eosinophils is in the normal range and the endoscopic biopsy is negative. Obtaining pathology of ascites as much as possible and taking a multisite biopsy sample, including both targeted and random biopsies, may improve the diagnostic rate.
Keywords: ascites; biopsy; diagnosis; eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Khan S, Orenstein SR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008;37:333–48, v. - PubMed
-
- Alhmoud T, Hanson JA, Parasher G. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: an underdiagnosed condition. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61:2585–92. - PubMed
-
- Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltim). 1970;49:299–319. - PubMed
-
- Hahn JW, Lee K, Shin JI, et al. Global incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis, 1976–2022: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:3270–84.e77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

