Linezolid in combination with pentazocine causes serotonin syndrome: A case report
- PMID: 40696580
- PMCID: PMC12282768
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043517
Linezolid in combination with pentazocine causes serotonin syndrome: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by autonomic and muscular hyperactivity resulting from the use of serotonergic drugs that bind to peripheral or central postsynaptic serotonin receptors. This syndrome can be easily confused with other clinical conditions, leading to delays in diagnosis and jeopardizing vital prognosis. Linezolid is utilized in the clinical management of gram-positive coccal infections, while pentazocine, an opioid analgesic, is frequently employed for pain relief in trauma patients. Currently, there are limited reports documenting the occurrence of SS associated with linezolid and pentazocine. In this report, we present the case of a 32-year-old man who developed SS following simultaneous administration of linezolid and pentazocine; his symptoms were effectively managed upon discontinuation of these medications.
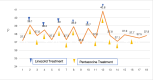
Patient concerns: A 32-year-old male patient was treated with pentazocine and linezolid for pain management related to trauma as well as for a gram-positive coccal infection. One hour after administration, he exhibited tremors in his right limb along with hand tremors, profuse sweating, and sinus tachycardia; his body temperature subsequently rose to 40°C. Laboratory tests including white blood cell count, procalcitonin levels, and C-reactive protein, showed no significant changes compared to previous results. A follow-up computed tomography scan of the head revealed no new ischemic lesions.
Diagnoses: The patient's physical examination, vital signs, and laboratory results were consistent with SS.
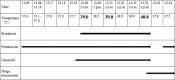
Interventions: Linezolid and pentazocine were discontinued immediately. Midazolam (3-6 µg/kg/h) and dexmedetomidine (0.1-0.3 µg/kg/h) were administered, and oral diazepam (2.5 mg 3 times daily) was gradually continued.
Outcomes: Following this treatment regimen, the patient's profuse sweating improved significantly, and he became stable overall; his body temperature gradually returned to normal levels. Subsequently, the patient was transferred from the surgical intensive care unit to a general ward after 7 days of treatment.
Lessons: Although SS is not very common in patients using pentazocine and linezolid separately, it is important because it is an emergency condition that can result in death if not treated appropriately. This clinical case highlights the importance of thoroughly understanding the clinical manifestations of SS to ensure early and appropriate treatment management.
Keywords: linezolid; pentazocine; serotonin; serotonin syndrome.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic interventions for treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 11;3(3):CD013130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013130.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35274741 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic treatment for non-tuberculous mycobacteria lung infection in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 27;3(3):CD016039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD016039. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40145528
-
Oral morphine for cancer pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 22;4(4):CD003868. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003868.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27105021 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Relapsing Hailey-Hailey Disease Displaying a Durable Complete Response to Hydroxyurea.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):168-169. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654217
References
-
- Ables AZ, Nagubilli R. Prevention, recognition, andmanagement of serotonin syndrome. Am fam physician. 2010;81:1139–42. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield JM, Lawrence KR, Reisman A, et al. Comparison of serotonin toxicity with concomitant use of linezolid or comparators and serotonergic agents: an analysis of Phase III and IV randomized clinical trial data. J Antimicrob Chemoth. 2011;67:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Dunkley EJ, Isbister GK, Sibbritt D, Dawson AH, Whyte IM. Thehunter serotonin toxicity criteria: Simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity. Qjm. 2003;96:635–42. - PubMed
-
- Radomski JW, Dursun SM, Reveley MA, Kutcher SP. An exploratory approach to the serotonin syndrome. Med hypotheses. 2000;55:218–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

