Comparing therapeutic effects across tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Chronic myeloid leukemia outcomes and analysis of influencing factors
- PMID: 40696584
- PMCID: PMC12282708
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043120
Comparing therapeutic effects across tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Chronic myeloid leukemia outcomes and analysis of influencing factors
Abstract
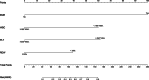
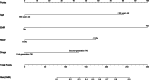
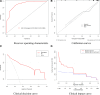
This study aims to comprehensively assess the effects of imatinib, nilotinib, and flumatinib in treating chronic myeloid leukaemia and to explore the main factors affecting its efficacy. Ninety-nine chronic myeloid leukaemia patients initially diagnosed and treated with one of these 3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors at a tertiary hospital in Shanxi Province between June 2018 and June 2023 were selected and divided into an imatinib group (n = 32), nilotinib group (n = 30), and flumatinib group (n = 37). Hematological response rates, cytogentic response rates, molecular response rates, and adverse reactions were compared among the 3 groups to statistically analyze efficacy and safety. Univariate analysis and logistic regression were used to explore the related factors influencing the curative effect. A nomogram prediction model of influencing factors of efficacy was constructed in R software and validated according to receiver operating characteristic and calibration curves, with a clinical decision curve and clinical impact curve further drawn to confirm its clinical practicability. The complete cytogenetic response at 3 months differed significantly, with rates of 53.13%, 76.67%, and 78.38% for the imatinib, nilotinib, and flumatinib groups, respectively (P < .05). Major molecular response (MMR) rates at 3 months were 25.00%, 53.33%, and 51.35%, reaching 78.13%, 90.00%, and 83.78% at 12 months, respectively. Deep molecular response (DMR) rates at 12 months were 50.00%, 76.67%, and 75.68% in each respective group (P < .05). Multivariate logistic regression indicated early molecular response, white blood cell count, red cell distribution width and platelet count as independent influencing factors of MMR. Age, drug type, early early molecular response, and red cell distribution width were identified as independent influencing factors of DMR (P < .05). The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves for MMR and DMR nomogram models were 0.912(95% confidence interval: 0.833, 0.990)and 0.874 (95% confidence interval: 0.801, 0.946), respectively, indicating satisfactory model calibration. Nilotinib and flumatinib demonstrate superior efficacy over imatinib, with effectiveness influenced by various factors including sociodemographic characteristics, clinical heterogeneity, and drug side effects. The proposed clinical prediction model may provide valuable insights for decision-making and demonstrates generalizability and practical application value.
Keywords: chronic myeloid leukaemia; efficacy; flumatinib; imatinib; influencing factors; nilotinib.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Qian XL. Prognostic value and efficacy analysis of BCR-ABL and significance of ABL kinase domain mutation in chronic myeloid leukemia after TKI treatment [D]. Soochow University. 2019.
-
- Yayun W, Hongguo Z, Zhongguang C, et al. 3-year clinical observation of dasatinib, nilotinib and imatinib in the treatment of newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Chin J Lab Hematology. 2015;23:356–63.
-
- Cheng YX. Application effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia [D]. Anhui Med Univ. 2016.
-
- Xiaoshuai Z, Yaqen Q, Yueyun L, et al. Combination of socio-demographic and clinical factors to predict treatment response and outcome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase. Chin J Hematol. 2021;43:54–62.
-
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

