Predictive and prognostic models and visualizations of distant metastasis in gallbladder cancer
- PMID: 40696595
- PMCID: PMC12282738
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043369
Predictive and prognostic models and visualizations of distant metastasis in gallbladder cancer
Abstract
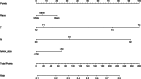
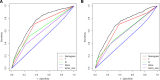
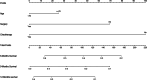
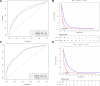
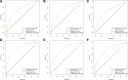
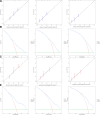
Employing multivariate statistical methods, we aimed to construct and validate predictive models for distant metastasis (DM) risk and overall survival (OS) in patients with gallbladder cancer (GBC), using data from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database maintained by the National Cancer Institute. These models were visualized through the development of intuitive nomograms. We extracted clinical data of all patients diagnosed with GBC between 2010 and 2015 from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. Both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted utilizing R software (Version 4.2.1) to identify independent risk predictors for DM in GBC patients, and univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to determine independent prognostic factors for OS among GBC patients with DM. The discriminatory capabilities and predictive accuracies of the developed nomograms were examined through calibration curves, receiver operating characteristic curves, and decision curve analysis. In our study, 3071 patients with GBC were included, of which 759 (24.72%) had DM. Race, T stage, N stage, and tumor size were identified as independent risk factors for DM, while age, surgical intervention, and chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors for OS in GBC patients with DM. The area under the curve for the prognostic nomogram reached 0.726 and 0.730 in the training and validation sets, respectively. The area under the curve for the same nomogram at 6, 9, and 12 months was 0.744, 0.740, and 0.704 for the training set, and 0.798, 0.774, and 0.776 for the validation set, respectively. The calibration curves, decision curve analysis, and Kaplan-Meier survival curves further demonstrated the effectiveness of the nomograms in predicting DM occurrence and the prognosis of GBC patients with DM. Race, T stage, N stage, and tumor size emerged as independent risk factors for DM in GBC patients; whereas age, surgical treatment, and chemotherapy were found to be independent prognostic factors for OS in GBC patients with DM. We successfully established and validated a predictive nomogram for DM occurrence and a prognostic nomogram for OS in GBC patients with DM, both showing high accuracy and clinical utility.
Keywords: SEER database; gallbladder cancer; metastasis; nomogram; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Schmidt MA, Marcano-Bonilla L, Roberts LR. Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and genetic risk associations. Chin Clin Oncol. 2019;8:31. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

