Construction of a prognostic model based on ferroptosis- and mitochondrial metabolism-related genes for patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 40696656
- PMCID: PMC12282778
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043307
Construction of a prognostic model based on ferroptosis- and mitochondrial metabolism-related genes for patients with breast cancer
Abstract
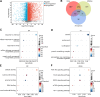
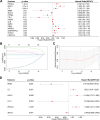
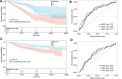
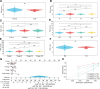
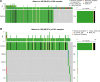
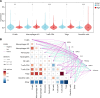
Mitochondrial metabolism (MM)-mediated ferroptosis plays a critical role in breast cancer (BC). However, the potential targets based on ferroptosis and MM in BC remain poorly understood. This study aimed to explore the prognostic role of ferroptosis- and MM-related genes (FPMMs) in BC. Differentially expressed FPMMs were identified, and functional analyses were performed. Univariate Cox, LASSO, and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to screen hub genes, and a prognostic risk model was then constructed and validated in external datasets. Gene set variation analysis was conducted to investigate their regulatory functions. Furthermore, immune infiltration analysis was performed using the "quantiseq" algorithm. We identified 206 differentially expressed FPMMs. A prognostic risk model consisting of 6 genes (BRD4, FLT3, SIAH2, CS, EMC2, and PI3KCA) was constructed, exhibiting good predictive capability and stability. These 6 prognostic genes were dysregulated in BC, with PI3KCA exhibiting the highest mutation frequency. Gene set variation analysis further revealed that the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling was suppressed in BC. In addition, the risk score based on the prognostic model was associated with immune infiltration, particularly with B cells, T cells, CD4, and dendritic cells. Our study highlights the potential of the prognostic model based on FPMMs as a valuable tool for BC prognosis prediction.
Keywords: breast cancer; ferroptosis; metabolism; mitochondrion; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ferroptosis-related LINC02535/has-miR-30c-5p/EIF2S1 axis as a novel prognostic biomarker involved in immune infiltration and progression of PDAC.Cell Signal. 2024 Nov;123:111338. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111338. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 39117252
-
[Ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA to predict the clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Jun 18;57(3):569-577. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.03.022. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40509836 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Integrated proteomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals key regulatory genes between ER-positive/PR-positive and ER-positive/PR-negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1048. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14451-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597935 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Mammographic density, endocrine therapy and breast cancer risk: a prognostic and predictive biomarker review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 26;10(10):CD013091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34697802 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

