Recurrent aphthous stomatitis, oxidative stress, and ischemia modified albumin: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40696698
- PMCID: PMC12282762
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043403
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis, oxidative stress, and ischemia modified albumin: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
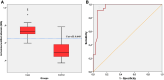
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by painful ulcers on the oral mucosa. Oxidative stress is held responsible for the pathogenesis of this disease of unknown etiology. In oxidative stress, the balance between oxidant-antioxidant substances changes in favor of the oxidative side. Ischaemia modified albumin (IMA) is a new type of albumin. It occurs as a result of factors such as ischemic attacks and oxidative stress. The aim of the study was to compare IMA levels in patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis with healthy volunteers and to investigate whether IMA has a diagnostic value in the disease. This cross-sectional study included 32 patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis and 34 healthy volunteers of similar age and sex. Albumin and IMA levels were determined by spectrophotometric albumin cobalt binding assay in venous blood samples on the same day. IMA was expressed as absorbance unit. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to determine whether IMA values could be a diagnostic marker for prediction of disease. IMA values of the patient group were significantly higher than IMA values of the control group (P < .001). IMA was statistically significant in the prediction of recurrent aphthous stomatitis (P < .001). The discrimination power for IMA was very good (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve 95% CI = 0.952 [0.897-1.000]). Recurrent aphthous stomatitis, in which oxidative stress plays a role in the etiopathogenesis, is closely associated with high IMA levels. IMA levels may have diagnostic value as an indicator of oxidative stress in the disease.
Keywords: ischemia modified albumin; oxidative stress; recurrent aphthous stomatitis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The author have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic and local effect of oxidative stress on recurrent aphthous stomatitis: systematic review.J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Apr;102(4):453-463. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02434-8. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38376817
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Common Oral Conditions: A Review.JAMA. 2024 Mar 26;331(12):1045-1054. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0953. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38530258 Review.
-
Colchicine efficacy on oral ulcers caused by Behçet's spectrum disorders including idiopathic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, PFAPA, and Behçet's Disease.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Jul 31;184(8):516. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06363-7. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40745400
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tugrul S, Koçyiğit A, Doğan R, et al. Total antioxidant status and oxidative stress in recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e130–135. - PubMed
-
- Yavuz C, Kurku H, Neşelioğlu S. The evaluation of thiol/disulphide homeostasis in recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Stanley HR. Aphthous lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972;33:407–16. - PubMed
-
- Del Mazo RC, Forcen LG, Aguilar MEN. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Med Clin (Barc). 2023;161:251–9. - PubMed
-
- Tsitu VM, Rallis D, Tsekova M, Yanev N. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Gen Med. 2023;25:60–70.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical