Association Between Irisin Level and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40696815
- PMCID: PMC12284321
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70662
Association Between Irisin Level and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Irisin is a newly discovered muscle factor, and more and more research has focused on the association between irisin and brain function. Our study aimed at investigating the correlation between irisin level and cognition.
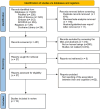
Methods: Five electronic databases were searched for the correlation between irisin level and cognition in humans. The primary outcome was the correlation between irisin level and global cognition. Secondary outcomes were the correlation between irisin level and each cognitive domain, the correlation between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level and global cognition, and the correlation between irisin level and BDNF level. Correlation coefficient (r) was used as effect size with its 95% confidence intervals (CI).
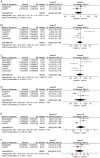
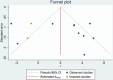
Results: There were a total of 11 articles that reported the correlation between irisin level and global cognition, and the pooled result showed a positive correlation among them (r = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.10-0.41). The subgroup analysis showed a positive correlation among non-Asians (r = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.16-0.40), studies with small sample size (r = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.20-0.49), irisin measured from both serum (r = 0.32, 95% CI: 0.15-0.49) and cerebrospinal fluid (r = 0.27, 95% CI: 0.03-0.50), scales using Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) (r = 0.36, 95% CI: 0.16-0.52), and study populations with diseases impairing cognition (r = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.07-0.43). Besides, our results indicated that there were no correlations between irisin level and cognitive domains, including immediate memory, short-term memory, executive function, attention, language, and visual spatial ability (all p > 0.05). Additionally, the results suggested a positive correlation between BDNF level and global cognitive function (r = 0.27, 95% CI: 0.12-0.42), as well as the correlation between irisin level and BDNF level (r = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.24-0.56).
Conclusions: This study implied that irisin has a positive effect on cognitive function, and the mechanism may be associated with promoting the expression of BDNF.
Keywords: cognitive function; irisin; meta‐analysis; systematic review.
© 2025 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Selegiline for Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD000442. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000442. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12535396
-
Reminiscence therapy for dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):CD001120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001120.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29493789 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Adilakshmi, P. , Suganthi V., Rao K. S., and Mahendran K. B.. 2023. “Effect of High‐Intensity Resistance Training Versus Endurance Training on Irisin and Adipomyokine Levels in Healthy Individuals: An 8‐Week Interventional Study.” Cureus 15, no. 10: e46483. 10.7759/cureus.46483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024KY927/Medical and Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province
- 00004FSYLB2023004/Medical Technology-14th Five-Year Plan Provincial First-Class Discipline
- KYQN2023002/The Basic Scientific Research Funds of Department of Education of Zhejiang Province
- Y202352824/The Project Supported by Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department
- Y202352929/The Project Supported by Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

