Butyrate, IL-4, and EP4 Receptors: A Triad of Colorectal Homeostasis, Protecting Against Onset of Cancer and IBD?
- PMID: 40697058
- PMCID: PMC12376015
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.70046
Butyrate, IL-4, and EP4 Receptors: A Triad of Colorectal Homeostasis, Protecting Against Onset of Cancer and IBD?
Abstract
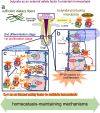
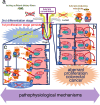
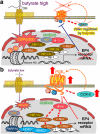
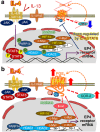
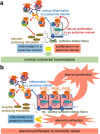
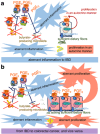
In this article, onset mechanisms of colorectal cancer and intestinal bowel diseases (IBD) are postulated to involve the aberrant expression/hyper-activation of E-type prostanoid 4 (EP4) receptors. Although prostaglandin E2 and EP4 receptors are important factors for maintaining colorectal homeostasis, their mediated signaling is also considered to be involved in the etiology of severe intestinal diseases. To prevent uncontrollable activations of EP4 receptors, two safety factors are proposed: butyrate as an external safety factor and interleukin (IL)-4 as an internal safety factor. Thus, for maintaining vulnerable colorectal homeostasis, the levels of EP4 receptors, butyrate, and IL-4 are proposed as an important triad for protecting against development/onset risks of, at least, EP4 receptor-mediated cancer and IBD.
Keywords: EP4 receptors; IBD; butyrate; colorectal cancer; colorectal homeostasis; interleukin‐4; prostaglandin E2.
© 2025 The Author(s). BioEssays published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short chain fatty acid butyrate uptake reduces expressions of prostanoid EP4 receptors and their mediation of cyclooxygenase-2 induction in HCA-7 human colon cancer cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 15;853:308-315. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30980797
-
Comparison of the Genomic Activity of an EP4-Receptor and β2-Adrenoceptor Agonist in BEAS-2B Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells: In Search of Compartmentalized, cAMP-Dependent Gene Expression.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Sep 18;391(1):64-81. doi: 10.1124/jpet.124.002226. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 39060164
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Strategies for detecting colon cancer and/or dysplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD000279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000279.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9:CD000279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000279.pub4. PMID: 16625534 Updated.
-
Strategies for detecting colon cancer and/or dysplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD000279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000279.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD000279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000279.pub3. PMID: 15106148 Updated.
References
-
- Fujino H., West K. A., and Regan J. W., “Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase‐3 and Stimulation of T‐Cell Factor Signaling Following Activation of EP2 and EP4 Prostanoid Receptors by Prostaglandin E2 ,” Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (2002): 2614–2619, 10.1074/jbc.M109440200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feddersen U. R., Hendel S. K., Berner‐Hansen M. A., Jepps T. A., Berner‐Hansen M., and Bindslev N., “Nanomolar EP4 Receptor Potency and Expression of Eicosanoid‐Related Enzymes in Normal Appearing Colonic Mucosa From Patients With Colorectal Neoplasia,” BMC Gastroenterology 22 (2022): 234, 10.1186/s12876-022-02311-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

