Clinical translation of 3D-printed patient-specific bone implants: a consensus statement
- PMID: 40697079
- PMCID: PMC12626479
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002944
Clinical translation of 3D-printed patient-specific bone implants: a consensus statement
Abstract
Background: Extensive defects in long bones, resulting from trauma, disease, or other etiologies, impose significant morbidity on patients and may necessitate amputation, long-term disability, or premature mortality. While 3D-printed, patient-specific implants offer promising regenerative solutions, their clinical implementation remains hindered by regulatory challenges, lack of standardized guidelines, and gaps in translational research. Addressing these barriers is critical to improving patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare resource utilization.
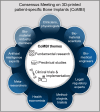
Materials and methods: A multidisciplinary group of 29 experts-including clinicians (surgeons, anesthesiologists), biomaterial scientists, biomedical engineers, legal/regulatory professionals, health economists, meta-researchers, artificial intelligence experts, trialists, and biomaterial industry representatives-convened for the Consensus Meeting on 3D-printed patient-specific Bone Implants (CoMBI). Preceding the meeting, key questions were discussed in individual interviews and categorized into fundamental research, preclinical studies, and clinical trials & implementation (CoMBI themes). Experts presented on each theme, followed by structured discussions. Statements were synthesized, iteratively refined, and validated through open review.
Results: The consensus meeting resulted in 20 key statements addressing the CoMBI themes, outlining a framework to advance regulatory compliance and facilitate the clinical adoption of 3D-printed implants. Key statements include the need for harmonized regulatory pathways, clear guidelines on preclinical validation, and innovative trial designs tailored to complex, patient-specific implants. Strengthening collaboration among policymakers, regulatory agencies, and clinicians is crucial to overcoming current implementation barriers and ensuring equitable patient access to these advanced technologies.
Conclusion: This Consensus Statement presents 20 key statements across fundamental research, preclinical studies, and clinical trials & implementation, offering a roadmap for accelerating the regulatory and clinical translation of 3D-printed patient-specific bone implants. The findings emphasize the critical role of interdisciplinary collaboration in overcoming challenges, such as standardizing implant development and navigating complex regulatory landscapes. By addressing these barriers and outlining practical strategies, the consensus highlights actionable steps to bridge the gap between innovation and clinical application.
Keywords: 3D-printed implants; bone defects; bone regeneration; consensus; interdisciplinary collaboration.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. D. W. Hutmacher is a cofounder of both BellaSeno GmbH and Osteopore International. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest. The funder (Volkswagen Foundation) had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures
References
-
- Woolf SH. The meaning of translational research and why it matters. JAMA 2008;299:211–13. - PubMed
-
- Dirnagl U, Duda GN, Grainger DW, et al. Reproducibility, relevance and reliability as barriers to efficient and credible biomedical technology translation. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 2022;182:114118. - PubMed
-
- Hutmacher DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials 2000;21:2529–43. - PubMed
-
- Hutmacher DW, Tandon B, Dalton PD. Chapter 11 - Scaffold design and fabrication. In: De Boer J, Cav B, Uquillas JA, Malik N, eds.. Tissue Engineering. Academic press; 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous