Gut microbiota and sepsis-associated encephalopathy: pathogenesis and precision therapies
- PMID: 40697274
- PMCID: PMC12279707
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1596467
Gut microbiota and sepsis-associated encephalopathy: pathogenesis and precision therapies
Abstract
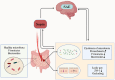
Sepsis is defined as a condition of immune dysregulation in response to an infection, and sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is often the initial symptom that manifests in patients with sepsis. This condition is characterized by its high mortality rates and the potential to cause significant disability among survivors. Despite its severity, the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to the development of SAE are not yet fully understood. Additionally, there are no established strict diagnostic criteria or potent treatment options available for this condition. However, an increasing body of evidence suggests that an imbalance in the gut microbiota is associated with SAE, potentially through the gut-brain axis (GBA). The GBA axis refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut microbiota and the central nervous system. In this review, we discuss the changes in the gut microbiota in SAE and the mechanisms of the GBA axis, involving neural, immune, endocrine, and neurotransmitter pathways. Finally, we conclude by evaluating the preclinical and clinical evidence for fecal microbiota transplantation and probiotics in SAE. Targeting the GBA axis will be an actionable target to ameliorate the development and progression of SAE.
Keywords: fecal microbiota transplantation; gut microbiota; probiotics; sepsis; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Copyright © 2025 Wei, Dai, Li, Zhou and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

