Tightrope vs. hook plate fixation for acute acromioclavicular joint dislocation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40697286
- PMCID: PMC12277739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xrrt.2025.04.002
Tightrope vs. hook plate fixation for acute acromioclavicular joint dislocation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Treatment for acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) dislocations aims to restore joint congruity and mechanical stability. However, the best operative technique remains a controversial issue. This systematic review and meta-analysis thus aim to compare the clavicular hook plate (HP) vs. the TightRope (TR) in the management of ACJ dislocation.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted using Embase, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science databases to retrieve all relevant studies. Outcomes were operative time (minutes), intraoperative blood loss (mL), clinical outcome measures, postoperative coracoclavicular distance (CCD), and complications. The methodological quality of studies was assessed using the Methodological Index for Nonrandomized Studies tool for nonrandomized studies, and the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool for randomized control trials.
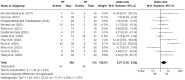
Results: The literature search yielded 221 studies, of which 12 studies enrolling a total of 683 patients were included in this review, with 371 in the HP group and 312 in the TR group. Meta-analysis of comparative studies between HP and TR fixation showed that HPs had better Constant-Murley scores (mean difference (MD), -3.56; 95% confidence interval (CI), -5.37 to -1.75; P = .0001), and less intraoperative blood losses (MD, 41.27; 95% CI, 30.67-51.87; P < .00001). Conversely, TR fixation had better visual analog scale scores (MD, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.34-0.76; P < .0001), and shorter postoperative CCD (MD, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.19-0.71; P = .0008). There was no significant difference in operative time (MD, 1.75; 95% CI, -16.55-20.05; P = .85), University of California, Los Angeles shoulder scores (MD, 0.34; 95% CI, -0.81 to 1.48; P = .56), American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons scores (MD, 0.39; 95% CI, -0.90 to 1.68; P = .55), and complications (OR, 2.57; 95% CI, 1.00-6.62; P = .05).
Conclusion: TR fixation in ACJ dislocations had similar operative times, complication rates, University of California, Los Angeles scores, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons scores to HP fixation. The HP group had less intraoperative blood loss and better Constant-Murley scores. Conversely, TR fixation had better visual analog scale scores and smaller postoperative CCD. Future randomized control trials on this subject would aid in increasing the validity of our findings.
Keywords: Acromioclavicular joint; Clavicle; Clavicular hook plate; Dislocation; Surgical treatment; TightRope.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Figures









References
-
- Balke M., Schneider M.M., Shafizadeh S., Bäthis H., Bouillon B., Banerjee M. Current state of treatment of acute acromioclavicular joint injuries in Germany: is there a difference between specialists and non-specialists? A survey of German trauma and orthopaedic departments. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:1447–1452. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2795-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

