Female athletes have high return to sport and low complication rates following ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) repair or reconstruction: a systematic review
- PMID: 40697295
- PMCID: PMC12277714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xrrt.2025.02.007
Female athletes have high return to sport and low complication rates following ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) repair or reconstruction: a systematic review
Abstract
Hypothesis and background: Ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) injuries can be caused by repetitive microtrauma, particularly in throwers and overhead athletes or from acute elbow trauma-producing excessive valgus stress. The current literature is male-dominated and may be a misguiding diagnosis and treatment of female UCL injuries, which are often traumatic or unrelated to overhead throwing. We hypothesized that UCL repair and reconstruction in female athletes are safe and effective procedures that enhance patients' ability to return to sports (RTS) with an acceptably low complication rate.
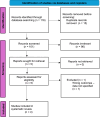
Methods: In accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched in July 2024 for studies published after 2000. Studies were included if they evaluated female athletes of any age range or level of competition who underwent UCL reconstruction or repair, reported RTS rates, complications, or reoperations and had a minimum of 2 years of follow-up time.
Results: The initial screen identified 116 studies, 4 of which were included in this systematic review. Each study had a retrospective study design with sufficiently low risk of bias. A total of 49 patients, all female, were included in this study. The mean age ranged from 15.3 to 22.2 years. Seventeen patients in 3 studies underwent UCL reconstruction. In addition, 2 studies included a total of 32 patients who underwent UCL repair. Numerous sports were represented in this study, the most popular of which were gymnastics, softball, and cheerleading. There was a cumulative 11.8% complication rate in UCL reconstruction patients and 3.1% cumulative complication rate in UCL repair patients. RTS rates for UCL repair and UCL reconstruction ranged from 86.7% to 94.1% and 33.3% to 76.9%, respectively.
Discussion and conclusion: UCL repair is an effective procedure in helping female athletes RTS with low complication rates. However, UCL reconstruction has more variable RTS rates in female athletes. Surgeons should be aware of the specific risk factors for UCL injury associated with women's sports, and treatment should be tailored to each athlete's specific goals.
Keywords: Elbow; Female athletes; Outcomes; Sex disparity; UCL reconstruction; UCL repair.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Azar F.M., Andrews J.R., Wilk K.E., Groh D. Operative treatment of ulnar collateral ligament injuries of the elbow in athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:16–23. - PubMed
-
- Barrentine S.W., Fleisig G.S., Whiteside J.A., Escamilla R.F., Andrews J.R. Biomechanics of windmill softball pitching with implications about injury mechanisms at the shoulder and elbow. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1998;28:405–414. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources