Rat Model of Granulomatous Mastitis
- PMID: 40697420
- PMCID: PMC12279910
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S537209
Rat Model of Granulomatous Mastitis
Abstract
Background: Granulomatous mastitis (GM) is an immune-related, clinically refractory disease, the translational research of which has been hindered by the lack of animal models. Establishing a stable rat model of GM is critical for elucidating its mechanisms and developing therapeutic approaches.
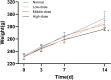
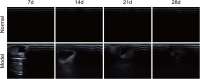
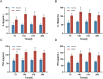
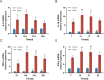
Methods: The first batch of rats was randomly divided into a normal group, a low-dose group (0.2 mL), a middle-dose group (0.4 mL), and a high-dose group (0.8 mL). Except for the normal group, the remaining groups were subjected to model establishment using a tissue homogenate-complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) suspension. The optimal dose was determined based on gross morphology, mammary inflammation index, and histopathological evaluation. The second batch of rats was modeled using the optimal dose, with a comparable number of normal rats as controls. At 7, 14, 21, and 28 days post-modeling, mammary gland appearance, histomorphology, and serum/tissue mRNA expression levels of key inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ, IL-2) were observed.
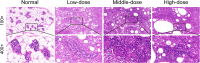
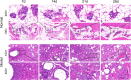
Results: Rats in the middle-dose group exhibited characteristic features of human GM, including gross morphological changes such as breast swelling, ulceration, and fistula formation. Histologically, granulomas characterized by epithelioid cells and Langhans multinucleated giant cells, along with persistent inflammatory cell infiltration, were observed. Compared with the parallel normal group, the expression levels of IL-2, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were significantly elevated in the model group, with their expression fluctuating over time.
Conclusion: The 0.4 mL tissue homogenate-CFA injection method successfully induced a stable, reproducible, and long-lasting rat model that closely mimics human GM. This model provides a robust foundational platform for future research.
Keywords: animal model; autoimmunity; granulomatous mastitis; tissue homogenate-CFA injection method.
© 2025 Gong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Hua C, Li F, Shi Y, et al. Long-term outcomes of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of granulomatous lobular mastitis: a two-year follow-up study on recurrence and new occurrence rates with analysis of risk factors. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:7389–7399. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S485589 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

